
123 OutLook Express Backup Enterprise Edition v1.20 by RiSE serial key or number

123 OutLook Express Backup Enterprise Edition v1.20 by RiSE serial key or number
| Freeware Utilities for Windows |
All the utilities and tools in this Web site are compressed in a ZIP file. If you don't have a software that can open a ZIP file, you can download the CAM UnZip utility. CAM UnZip is a small freeware utility that allows you to easily extract files from any ZIP file. You can also download 7-Zip archive manager - very good archive manager that allows you to open ZIP files and others archive formats.
For more information about installing the utilities at this Web site, click here
If you want to add one or more of the following utilities into your Web site, click here
See Also:
Search in NirSoft Web site:
You can also easily jump to the right utilities section:
Password Recovery Utilities
Network Monitoring Tools
Web Browser Tools
Video/Audio Related Utilities
Internet Related Utilities
Desktop Utilities
Outlook/Office Utilities
Programmer Tools
Disk Utilities
System Utilities
Other Utilities
| Password Recovery Utilities |
WebBrowserPassView v2.07 WebBrowserPassView is a password recovery tool that reveals the passwords stored by the following Web browsers: Internet Explorer (Version 4.0 - 8.0), Mozilla Firefox (All Versions), Google Chrome, and Opera. This tool can be used to recover your lost/forgotten password of any Website, including popular Web sites, like Facebook, Yahoo, Google, and GMail, as long as the password is stored by your Web Browser. After retrieving your lost passwords, you can save them into text/html/csv/xml file, by using the 'Save Selected Items' option (Ctrl+S). |
| IE PassView v1.42 IE PassView is a small utility that reveals the passwords stored by Internet Explorer browser. It supports the new Internet Explorer 7.0-11.0, as well as older versions of Internet explorer, v4.0 - v6.0 |
| PasswordFox v1.66 PasswordFox is a small password recovery tool that allows you to view the user names and passwords stored by Mozilla Firefox Web browser. By default, PasswordFox displays the passwords stored in your current profile, but you can easily select to watch the passwords of any other Firefox profile. For each password entry, the following information is displayed: Record Index, Web Site, User Name, Password, User Name Field, Password Field, and the Signons filename. |
ChromePass v1.52 ChromePass is a small password recovery tool that allows you to view the user names and passwords stored by Google Chrome Web browser. For each password entry, the following information is displayed: Origin URL, Action URL, User Name Field, Password Field, User Name, Password, and Created Time. You can select one or more items and then save them into text/html/xml file or copy them to the clipboard. |
WirelessKeyView v2.11 WirelessKeyView recovers all wireless network keys (WEP/WPA) stored in your computer by the 'Wireless Zero Configuration' service of Windows XP and by the 'WLAN AutoConfig' service of Windows Vista. It allows you to easily save all keys to text/html/xml file, or copy a single key to the clipboard. |
| Network Password Recovery v1.55 When you connect to a network share on your LAN or to your .NET Passport/Messenger account, Windows XP/Vista allows you to save your password in order to use it in each time that you connect the remote server. This utility recovers all network passwords stored on your system for the current logged-on user. |
| BulletsPassView v1.32 BulletsPassView is a password recovery tool that reveals the passwords stored behind the bullets in the standard password text-box of Windows operating system and Internet Explorer Web browser. After revealing the passwords, you can easily copy them to the clipboard or save them into text/html/csv/xml file. |
| Mail PassView v1.91 - Email Password Recovery Recovers the passwords and other email accounts information of the following email applications: Outlook Express, Microsoft Outlook 2000 (POP3/SMTP Accounts only), Microsoft Outlook 2002/2003/2007/2010/2013/2016, Windows Mail, IncrediMail, Eudora, Netscape Mail, Mozilla Thunderbird, |
| PstPassword v1.20 PstPassword is a small utility that recover lost password of Outlook .PST (Personal Folders) file. |
| RouterPassView v1.89 Most modern routers allow you to backup the configuration of the router into a file, and then restore the configuration from the file when it's needed. The backup file of the router usually contains important data like your ISP user name/password, the login password of the router, and wireless network keys. If you lost one of these password/keys, but you still have a backup file of your router configuration, RouterPassView might help you to recover your lost password from your router file. |
| VaultPasswordView v1.10 VaultPasswordView is a simple tool for Windows 10/8/7 that decrypts and displays the passwords and other data stored inside 'Windows Vault'. You can use it to decrypt the Windows Vault data of your currently running system, as well as the Windows Vault data stored on external hard drive. |
| CredentialsFileView v1.10 CredentialsFileView is a simple tool for Windows that decrypts and displays the passwords and other data stored inside Credentials files of Windows. You can use it to decrypt the Credentials data of your currently running system, as well as the Credentials data stored on external hard drive. |
| EncryptedRegView v1.03 EncryptedRegView is a tool for Windows that scans the Registry of your current running system or the Registry of external hard drive you choose and searches for data encrypted with DPAPI (Data Protection API). When it finds encrypted data in the Registry, it tries to decrypt it and displays the decrypted data in the main window of EncryptedRegView. With this tool, you may find passwords and other secret data stored in the Registry by Microsoft products as well as by 3-party products. |
| DataProtectionDecryptor v1.10 DataProtectionDecryptor is a powerful tool for Windows that allows you to decrypt passwords and other information encrypted by the DPAPI (Data Protection API) system of Windows operating system. You can use this tool to decrypt DPAPI data on your current running system and to decrypt DPAPI data stored on external hard drive. |
| Remote Desktop PassView v1.02 Remote Desktop PassView is a small utility that reveals the password stored by Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection utility inside .rdp files. |
| SecurityQuestionsView v1.00 SecurityQuestionsView is a tool for Windows 10 that allows you to view the security questions and their answers stored in the Registry by Windows 10 operating system. SecurityQuestionsView can decrypt the security questions stored on your current running system (Requires elevation) and it can also decrypt the security questions stored on external hard drive. SecurityQuestionsView displays the security questions of all users on your system that chose to set their security questions, for every user there are usually 3 questions. |
| OperaPassView v1.10 OperaPassView is a small password recovery tool that decrypts the content of the Opera Web browser password file (wand.dat) and displays the list of all Web site passwords stored in this file. You can easily select one or more passwords in the OperaPassView window, and then copy the passwords list to the clipboard and save it into text/html/csv/xml file. |
| LSASecretsView v1.25 LSASecretsView is a small utility that displays the list of all LSA secrets stored in the Registry on your computer. The LSA secrets key is located under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Security\Policy\Secrets and may contain your RAS/VPN passwords, Autologon password, and other system passwords/keys. |
| LSASecretsDump v1.21 LSASecretsDump is a small console application that extract the LSA secrets from the Registry, decrypt them, and dump them into the console window. The LSA secrets key is located under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Security\Policy\Secrets and may contain your RAS/VPN passwords, Autologon password, and other system passwords/keys. This utility is the console version of LSASecretsView. |
| PCAnywhere PassView v1.11 Reveals the passwords stored in PCAnywhere items. Both login information and the protection passwords are revealed instantly. |
| Access PassView v1.12 This utility reveals the database password of every password-protected mdb file that created with Microsoft Access 95/97/2000/XP or with Jet Database Engine 3.0/4.0 It can be very useful if you forgot your Access Database password and you want to recover it. |
| Win9x PassView v1.1 The Win9x PassView utility reveals the passwords stored on your computer by Windows 95/98 operating system. |
| Content Advisor Password Remover v1.01 Removes the Content Advisor password in Internet Explorer (versions 4.x and above). Visual C++ Source code is included. |
| Enterprise Manager PassView v1.00 Reveals the passwords that SQL Server Enterprise Manager stores on your computer. |
| VNCPassView v1.05 VNCPassView is a small utility that recover the passwords stored by the VNC tool. It can recover 2 of passwords: password stored for the current logged-on user (HKEY_CURRENT_USER in the Registry), and password stored for the all users. |
| Dialupass v3.61 - Dialup Password Recovery This utility enumerates all dialup/VPN entries on your computers, and displays their logon details: User Name, Password, and Domain. You can use it to recover a lost password of your Internet connection or VPN. Dialupass also allows you to save the dialup/VPN list into text/html/csv/xml file, or copy it to the clipboard. |
| MessenPass v1.43 - Instant Messenger Password Recovery MessenPass is a password recovery tool that reveals the passwords of the following instant messenger applications: MSN Messenger, Windows Messenger (In Windows XP), Windows Live Messenger (In Windows XP And Vista), Yahoo Messenger (Version 5.x/6.x), ICQ Lite 4.x/5.x/2003, AOL Instant Messenger, AIM 6.x, AIM Pro, Trillian, Miranda, and GAIM. |
| AsterWin IE v1.03 This utility reveals the passwords stored behind the asterisks in the web pages of Internet Explorer 5.0 and above. You can use it for recovering a lost web site password, if it's stored on your computer. It was developed in Visual Basic environment and requires the Visual Basic Runtime library. Source code is included ! |
SmartSniff v2.29 SmartSniff allows you to capture TCP/IP packets that pass through your network adapter, and view the captured data as sequence of conversations between clients and servers. You can view the TCP/IP conversations in Ascii mode (for text-based protocols, like HTTP, SMTP, POP3 and FTP.) or as hex dump. (for non-text base protocols, like DNS) |
WifiChannelMonitor v1.60 WifiChannelMonitor captures wifi traffic on the channel you choose, using Microsoft Network Monitor capture driver in monitor mode, and displays extensive information about access points and the wifi clients connected to them. WifiChannelMonitor also allows you to view the information about wifi clients that are not connected to any access points, including the list of SSIDs (network names) that they are trying to connect. For every access point, the following information is displayed: SSID, MAC Address, Device Manufacturer , PHY Type, Channel, RSSI, Security, Beacons Count, Probe Responses Count, Data Bytes, Retransmitted Data Bytes, and more... For every client, the following information is displayed: MAC Address, Device Manufacturer, SSID list that the client tries to connect, Sent Data Bytes, Received Data Bytes, Probe Requests Count, and more... |
NetworkTrafficView v2.30 NetworkTrafficView is a network monitoring tool that captures the packets pass through your network adapter, and displays general statistics about your network traffic. The packets statistics is grouped by the Ethernet Type, IP Protocol, Source/Destination Addresses, and Source/Destination ports. For every statistics line, the following information is displayed: Ethernet Type (IPv4, IPv6, ARP), IP Protocol (TCP, UDP, ICMP), Source Address, Destination Address, Source Port, Destination Port, Service Name (http, ftp, and so on), Packets Count, Total Packets Size, Total Data Size, Data Speed, Maximum Data Speed, Average Packet Size, First/Last Packet Time, Duration, and process ID/Name (For TCP connections). |
HTTPNetworkSniffer v1.63 HTTPNetworkSniffer is a packet sniffer tool that captures all HTTP requests/responses sent between the Web browser and the Web server and displays them in a simple table. For every HTTP request, the following information is displayed: Host Name, HTTP method (GET, POST, HEAD), URL Path, User Agent, Response Code, Response String, Content Type, Referer, Content Encoding, Transfer Encoding, Server Name, Content Length, Cookie String, and more... You can easily select one or more HTTP information lines, and then export them to text/html/xml/csv file or copy them to the clipboard and then paste them into Excel. |
AppNetworkCounter v1.40 AppNetworkCounter is a simple tool for Windows that counts and displays the number of TCP/UDP bytes and packets sent and received by every application on your system. For every application, the following information is displayed: the number of sent and received bytes, number of sent and received packets, number of sent/received IPv4 bytes, and number of sent/received IPv6 bytes. It also displays the version information of the application - Product Name, Product Version, File Description, and Company Name. |
LiveTcpUdpWatch v1.32 LiveTcpUdpWatch is a tool for Windows that displays live information about all TCP and UDP activity on your system. Every line in the main table of LiveTcpUdpWatch displays the protocol (TCP/UDP/IPv4/IPv6), local/remote IP address, local/remote port, number of sent/received bytes, number of sent/received packets, connect/disconnect time (For TCP only), and the process (ID and path) responsible for this activity. |
PingInfoView v2.05 PingInfoView is a small utility that allows you to easily ping multiple host names and IP addresses, and watch the result in one table. It automatically ping to all hosts every number of seconds that you specify, and displays the number of succeed and failed pings, as well as the average ping time. You can also save the ping result into text/html/xml file, or copy it to the clipboard. |
WifiInfoView v2.65 WifiInfoView scans the wireless networks in your area and displays extensive information about them, including: Network Name (SSID), MAC Address, PHY Type (802.11g or 802.11n), RSSI, Signal Quality, Frequency, Channel Number, Maximum Speed, Company Name, Router Model and Router Name (Only for routers that provides this information), and more... When you select a wireless network in the upper pane of this tool, the lower pane displays the Wi-Fi information elements received from this device, in hexadecimal format. WifiInfoView also has a summary mode, which displays a summary of all detected wireless networks, grouped by channel number, company that manufactured the router, PHY type, or the maximum speed. |
SocketSniff v1.11 SocketSniff allows you to watch the Windows Sockets (WinSock) activity of the selected process. For each created socket, the following information is displayed: socket handle, socket type, local and remote addresses, local and remote ports, total number of send/receive bytes, and more. You can also watch the content of each send or receive call, in Ascii mode or as Hex Dump. |
CurrPorts v2.62 CurrPorts is a network monitoring software that displays the list of all currently opened TCP/IP and UDP ports on your local computer. For each port in the list, information about the process that opened the port is also displayed, including the process name, full path of the process, version information of the process (product name, file description, and so on), the time that the process was created, and the user that created it. In addition, CurrPorts allows you to close unwanted TCP connections, kill the process that opened the ports, and save the TCP/UDP ports information to HTML file , XML file, or to tab-delimited text file. CurrPorts also automatically mark with pink color suspicious TCP/UDP ports owned by unidentified applications (Applications without version information and icons) |
| TcpLogView v1.32 TcpLogView is a simple utility that monitors the opened TCP connections on your system, and adds a new log line every time that a TCP connection is opened or closed. For every log line, the following information is displayed: Even Time, Event Type (Open, Close, Listen), Local Address, Remote Address, Remote Host Name, Local Port, Remote Port, Process ID, Process Name, and the country information of the Remote IP (Requires to download IP to country file separately.) |
ProcessTCPSummary v1.11 ProcessTCPSummary is a simple tool for Windows that displays a summary of all process that have TCP connections or listening UDP ports. For every process, this tool displays the total number of TCP connections, number of TCP connections for each status (Established, Listening, Syn-Sent, Syn-Received...), number of IPv4 TCP connections, number of IPv6 TCP connections, common port numbers, and more... If you run ProcessTCPSummary as Administrator, you can also watch the number of TCP/UDP bytes sent and received by every process as well as the current send/receive speed. |
NetworkConnectLog v1.12 NetworkConnectLog is a simple utility that repeatedly scans your local area network (Using ARP and Netbios protocols) and add a new log line every time that a new computer or device connects to your network, and when a computer or device disconnects from your network. After the connect/disconnect log lines are accumulated, you can easily export the log lines to comma-delimited/tab-delimited/html/xml file. |
NetworkLatencyView v1.65 NetworkLatencyView is a simple tool for Windows that listens to the TCP connections on your system and calculates the network latency (in milliseconds) for every new TCP connection detected on your system. For every IP address, NetworkLatencyView displays up to 10 network latency values, and their average. The latency value calculated by NetworkLatencyView is very similar to the result you get from pinging to the same IP address. NetworkLatencyView also allows you to easily export the latency information to text/csv/tab-delimited/html/xml file, or copy the information to the clipboard and then paste it to Excel or other application. |
DNSQuerySniffer v1.81 DNSQuerySniffer is a network sniffer utility that shows the DNS queries sent on your system. For every DNS query, the following information is displayed: Host Name, Port Number, Query ID, Request Type (A, AAAA, NS, MX, and so on), Request Time, Response Time, Duration, Response Code, Number of records, and the content of the returned DNS records. You can easily export the DNS queries information to csv/tab-delimited/xml/html file, or copy the DNS queries to the clipboard, and then paste them into Excel or other spreadsheet application. |
WhoIsConnectedSniffer v1.25 WhoIsConnectedSniffer is a network discovery tool that listens to network packets on your network adapter using a capture driver (WinpCap or MS network monitor) and accumulates a list of computer and devices currently connected to your network. WhoIsConnectedSniffer uses various protocols to detect the computers connected to your network, including ARP, UDP, DHCP, mDNS, and BROWSER. For every detected computer or device, the following information is displayed: (Some of the fields might be empty if the information cannot be found inside the packets) IP Address, MAC Address, name of the device/computer, description, Operating System, Network Adapter Company, IPv6 Address. After collecting the connected computers/devices information, you can easily export the list to tab-delimited/comma-delimited/xml/html file. |
Wireless Network Watcher v2.22 Wireless Network Watcher is a small utility that scans your wireless network and displays the list of all computers and devices that are currently connected to your network. For every computer or device that is connected to your network, the following information is displayed: IP address, MAC address, the company that manufactured the network card, and optionally the computer name. You can also export the connected devices list into html/xml/csv/text file, or copy the list to the clipboard and then paste into Excel or other spreadsheet application. |
| NetworkUsageView v1.20 NetworkUsageView extracts and displays the network usage information stored in the SRUDB.dat database of Windows 8 and Windows 10. The network usage data is collected every hour by Windows operating systems and includes the following information: The name and description of the service or application, the name and SID of the user, the network adapter, and the total number of bytes sent and received by the specified service/application. |
WakeMeOnLan v1.86 This utility allows you to easily turn on one or more computers remotely by sending Wake-on-LAN (WOL) packet to the remote computers. When your computers are turned on, WakeMeOnLan allows you to scan your network, and collect the MAC addresses of all your computers, and save the computers list info a file. Later, when your computers are turned off or in standby mode, you can use the stored computers list to easily choose the computer you want to turn on, and then turn on all these computers with a single click. WakeMeOnLan also allows you to turn on a computer from command-line, by specifying the computer name, IP address, or the MAC address of the remote network card. |
| NetworkCountersWatch v1.02 NetworkCountersWatch is a tool for Windows that displays system counters for every network interface on your system. The system counters include the number of incoming/outgoing bytes, number of incoming/outgoing packets, number of broadcast packets, and more. You can also initialize all counters to zero at any time in order to watch the network counters for specific event. NetworkCountersWatch also calculates and displays the current download speed and upload speed on your network interface. |
WifiHistoryView v1.56 WifiHistoryView is a simple tool for Windows 10/8/7/Vista that displays the history of connections to wireless networks on your computer. For every event that the computer connected to a wireless network or disconnected from it, the following information is displayed: The date/time that the event occurred, network name (SSID), profile name, network adapter name, BSSID of the router/Access Point, and more... WifiHistoryView can read the wifi history information from a running system or from external event log file of another computer. |
NetworkOpenedFiles v1.35 NetworkOpenedFiles is a simple tool for Windows that displays the list of all files that are currently opened by other computers on your network. For every opened filename, the following information is displayed: Filename, user name, computer name (On Windows 7/2008 or later), Permissions information (Read/Write/Create), locks count, file owner, file size, file attributes, and more... |
NetBScanner v1.11 NetBScanner is a network scanner tool that scans all computers in the IP addresses range you choose, using NetBIOS protocol. For every computer located by this NetBIOS scanner, the following information is displayed: IP Address, Computer Name, Workgroup or Domain, MAC Address, and the company that manufactured the network adapter (determined according to the MAC address). NetBScanner also shows whether a computer is a Master Browser. You can easily select one or more computers found by NetBScanner, and then export the list into csv/tab-delimited/xml/html file. |
| WirelessNetView v1.75 WirelessNetView is a small utility that runs in the background, and monitor the activity of wireless networks around you. For each detected network, it displays the following information: SSID, Last Signal Quality, Average Signal Quality, Detection Counter, Authentication Algorithm, Cipher Algorithm, and more. |
| WirelessConnectionInfo v1.13 WirelessConnectionInfo is a simple tool for Windows Vista/7/8/2008 that displays general information and statistics about the active wifi connection, including the SSID, BSSID, PHY Type, Signal Quality, Receiving rate, Transmission Rate, Authentication Algorithm, Channel Number, Total number of transmitted/received frames, and more... |
| AdapterWatch v1.05 AdapterWatch displays useful information about your network adapters: IP addresses, Hardware address, WINS servers, DNS servers, MTU value, Number of bytes received or sent, The current transfer speed, and more. In addition, it displays general TCP/IP/UDP/ICMP statistics for your local computer. |
| NetResView v1.27 NetResView is a small utility that displays the list of all network resources (computers, disk shares, and printer shares) on your LAN. As opposed to "My Network Places" module of Windows, NetResView display all network resources from all domains/workgroups in one screen, and including admin/hidden shares. |
| NetRouteView v1.30 NetRouteView is a GUI alternative to the standard route utility (Route.exe) of Windows operating system. It displays the list of all routes on your current network, including the destination, mask, gateway, interface IP address, metric value, type, protocol, age (in seconds), interface name, and the MAC address. NetRouteView also allows you to easily add new routes, as well as to remove or modify existing static routes. |
CountryTraceRoute v1.31 CountryTraceRoute is a Traceroute utility, similar to the tracert tool of Windows, but with graphical user interface, and it's also much faster than tracert of Windows. CountryTraceRoute also displays the country of the owner of every IP address found in the Traceroute. After the Traceroute is completed, you can select all items (Ctrl+A) and then save them into csv/tab-delimited/html/xml file with 'Save Selected Items' option (Ctrl+S) or copy them to the clipboard (Ctrl+C) and then paste the result into Excel or other spreadsheet application. |
SniffPass v1.13 - Password Sniffer SniffPass is small utility that listens to your network, capture the passwords that pass through your network adapter, and display them on the screen instantly. SniffPass can capture the passwords of the following Protocols: POP3, IMAP4, SMTP, FTP, and HTTP (basic authentication passwords). You can use this utility to recover lost Web/FTP/Email passwords. |
BrowsingHistoryView v2.41 BrowsingHistoryView is a utility that reads the history data of 4 different Web browsers (Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, and Safari) and displays the browsing history of all these Web browsers in one table. The browsing history table includes the following information: Visited URL, Title, Visit Time, Visit Count, Web browser and User Profile. BrowsingHistoryView allows you to watch the browsing history of all user profiles in a running system, as well as to get the browsing history from external hard drive. You can also export the browsing history into csv/tab-delimited/html/xml file from the user interface, or from command-line, without displaying any user interface. |
BrowserDownloadsView v1.25 BrowserDownloadsView is a tool for Windows that displays the details of downloaded files of Chrome and Firefox Web browsers. For every download, the following information is displayed: Filename, Download URL, Web Page URL, Start Time, End Time, Download Duration, Download Size, Web Browser, and more... BrowserDownloadsView allows you to load the downloads list from your current running system (your user or all user profiles), from remote computer on your network , and from external hard drive. After BrowserDownloadsView loads the downloads list, you can select one or more downloads and then export them to comma-delimited/tab-delimited/html5/xml/JSON file or calculate the MD5/SHA1/SHA256/SHA512 hash of the downloaded files. |
WebCacheImageInfo v1.30 WebCacheImageInfo is a simple tool that searches for JPEG images with EXIF information stored inside the cache of your Web browser (Internet Explorer, Firefox, or Chrome), and then it displays the list of all images found in the cache with the interesting information stored in them, like the software that was used to create the image, the camera model that was used to photograph the image, and the date/time that the image was created. |
ImageCacheViewer v1.20 ImageCacheViewer is a simple tool that scans the cache of your Web browser (Internet Explorer, Firefox, or Chrome), and lists the images displayed in the Web sites that you recently visited. For every cached image file, the following information is displayed: URL of the image, Web browser that was used to visit the page, image type, date/time of the image, browsing time, and file size. When selecting a cache item in the upper pane of ImageCacheViewer, the image is displayed in the lower pane, and you can copy the image to the clipboard by pressing Ctrl+M. |
FBCacheView v1.20 FBCacheView is a simple tool that scans the cache of your Web browser (Internet Explorer, Firefox, or Chrome), and lists all images displayed in Facebook pages that you previously visited, including profile pictures, images uploaded to Facebook, and images taken from other Web sites. For every Facebook image, the following information is displayed: URL of the image, Web browser that was used to visit the page, image type, date/time of the image, visit time, image file size, and external URL (For images taken from another Web site). |
BrowserAddonsView v1.22 BrowserAddonsView is a simple tools that displays the details of all Web browser addons/plugins installed in your system. BrowserAddonsView can scan and detect the addons of most popular Web browsers: Chrome, Firefox, and Internet Explorer. For Chrome and Firefox, BrowserAddonsView detects and scans all Web browser profiles if there are multiple profiles. |
| IECacheView v1.58 - Internet Explorer Cache Viewer IECacheView is a small utility that reads the cache folder of Internet Explorer, and displays the list of all files currently stored in the cache. For each cache file, the following information is displayed: Filename, Content Type, URL, Last Accessed Time, Last Modified Time, Expiration Time, Number Of Hits, File Size, Folder Name, and full path of the cache filename. You can easily save the cache information into text/html/xml file, or copy the cache table to the clipboard and then paste it to another application, like Excel or OpenOffice Spreadsheet. |
EdgeCookiesView v1.17 EdgeCookiesView is a tool for Windows that displays the cookies stored by newer versions of Microsoft Edge Web browser (Starting from Fall Creators Update 1709 of Windows 10). It also allows you to select one or more cookies and then export them to tab-delimited, csv file, html file, or to a file in cookies.txt format. You can read the cookies from the current running system or from the WebCacheV01.dat database on external hard drive. |
| IECookiesView v1.79 This utility displays the details of all cookies that Internet Explorer stores on your computer. In addition, it allows you to change the content of the cookies, delete unwanted cookies files, save the cookies into a readable text file, find cookies by specifying the domain name, view the cookies of other users and in other computers, and more... Read More >> |
WebCookiesSniffer v1.30 WebCookiesSniffer is a packet sniffer tool that captures all Web site cookies sent between the Web browser and the Web server and displays them in a simple cookies table. The upper pane of WebCookiesSniffer displays the cookie string and the Web site/host name that sent or received this cookie. When selecting a cookie string in the upper pane, WebCookiesSniffer parses the cookie string and displays the cookies as name-value format in the lower pane. |
| IEHistoryView v1.70 This utility reads all information from the history file on your computer, and displays the list of all URLs that you have visited with Internet Explorer browser in the last few days. It also allows you to select one or more URL addresses, and then remove them from the history file or save them into text, HTML or XML file. In addition, you are allowed to view the visited URL list of other user profiles on your computer, and even access the visited URL list on a remote computer, as long as you have permission to access the history folder. |
| MZCookiesView v1.58 MZCookiesView is an alternative to the standard 'Cookie Manager' provided by Netscape and Mozilla browsers. It displays the details of all cookies stored inside the cookies file (cookies.txt) in one table, and allows you to save the cookies list into text, HTML or XML file, delete unwanted cookies, and backup/restore the cookies file. |
| MZHistoryView v1.65 MZHistoryView is a small utility that reads the history data file (history.dat) of Firefox/Mozilla/Netscape Web browsers, and displays the list of all visited Web pages in the last days. For each visited Web page, the following information is displayed: URL, First visit date, Last visit date, Visit counter, Referrer, Title, and Host name. You can also easily export the history data to text/HTML/Xml file. |
MZCacheView v2.00 MZCacheView is a small utility that reads the cache folder of Firefox/Mozilla/Netscape Web browsers, and displays the list of all files currently stored in the cache. For each cache file, the following information is displayed: URL, Content type, File size, Last modified time, Last fetched time, Expiration time, Fetch count, Server name, and more. You can easily select one or more items from the cache list, and then extract the files to another folder, or copy the URLs list to the clipboard. |
FirefoxDownloadsView v1.40 This utility displays the list of the latest files that you downloaded with Firefox. For every download record, the following information is displayed: Download URL, Download Filename (with full path), Referrer, MIME Type, File Size, Start/End Time, Download Duration, and Average Download Speed. You can easily select one or more downloads, and then save the list into xml/html/text/csv file or copy the downloads information to the clipboard and paste it into Excel or other spreadsheet application. |
| ChromeCookiesView v1.61 ChromeCookiesView is an alternative to the standard internal cookies viewer of Google Chrome Web browser. it displays the list of all cookies stored by Google Chrome Web browser, and allows you to easily delete unwanted cookies. It also allows you export the cookies into text/csv/html/xml file. For every cookie, the following information is displayed: Host Name, Path, Name, Value, Secure (Yes/No), HTTP Only Cookie (Yes/No), Last Accessed Time, Creation Time, Expiration Time. |
ChromeHistoryView v1.42 ChromeHistoryView is a small utility that reads the history data file of Google Chrome Web browser, and displays the list of all visited Web pages in the last days. For each visited Web page, the following information is displayed: URL, Title, Visit Date/Time, Number of visits, number of times that the user typed this address (Typed Count), Referrer, and Visit ID. You can select one or more history items, and them export them into html/xml/csv/text file, or copy the information to the clipboard and paste it into Excel. |
| SafariHistoryView v1.01 SafariHistoryView is a simple utility for Windows that reads and parses the history file of Safari Web browser (history.plist) and displays the browsing history in a simple table. Every browsing history line includes the following information: URL, Web Page Title, Last Visit Time, Visit Count, Redirected To URL, and Record Index. SafariHistoryView allows you to easily export the browsing history data into text/csv/html/xml file, or copy the data to the clipboard and then paste it into Excel. |
SafariCacheView v1.11 SafariCacheView is a simple utility for Windows that reads and parses the cache file of Safari Web browser (cache.db) and displays the list of all cached files in a simple table. Every cache information line includes the following information: Filename, Content Type, URL, Content Length, Server Name, Server Time, Expiration Time, Last Modified Time, Content Encoding, and Referrer. SafariCacheView also allows you to select one or more cache items and then extract them into the desired folder or save the cache list into html/text/xml/csv file. |
| OperaCacheView v1.40 OperaCacheView is a small utility that reads the cache folder of Opera Web browser, and displays the list of all files currently stored in the cache. For each cache file, the following information is displayed: URL, Content type, File size, Last accessed time, and last modified time in the server. You can easily select one or more items from the cache list, and then extract the files to another folder, or copy the URLs list to the clipboard. |
ChromeCacheView v2.21 ChromeCacheView is a small utility that reads the cache folder of Google Chrome Web browser, and displays the list of all files currently stored in the cache. For each cache file, the following information is displayed: URL, Content type, File size, Last accessed time, Expiration time, Server name, Server response, and more. You can easily select one or more items from the cache list, and then extract the files to another folder, or copy the URLs list to the clipboard. |
| FlashCookiesView v1.15 FlashCookiesView is a small utility that displays the list of cookie files created by Flash component (Local Shared Object) in your Web browser. For each cookie file, the lower pane of FlashCookiesView displays the content of the file in readable format or as Hex dump. You can also select one or more cookie files, and then copy them to the clipboard, save them to text/html/xml file or delete them. |
| MyLastSearch v1.65 MyLastSearch utility scans the cache and history files of your Web browser, and locate all search queries that you made with the most popular search engines (Google, Yahoo and MSN). The search queries that you made are displayed in a table with the following columns: Search Text, Search Engine, Search Time, Web Browser, and the search URL. |
| URLStringGrabber v1.11 URLStringGrabber is a small utility that scans all opened windows of Internet Explorer and grab the URLs stored in them, including clickable links, images, script files, CSS files, RSS feeds, and flash (.swf) files. The URLs list is displayed in table, and you can easily export some of the URLs or the entire URLs list into text, csv, html, or xml file. You can also copy the URLs list into the clipboard and paste them into Excel or other spreadsheet application. |
| IEDesignMode v1.00 IEDesignMode Adds a new menu item into the context menu of Internet Explorer that allows you to easily switch the active Internet Explorer window to design mode. When a Web page in in design mode, you can change the location of images and other objects, change the current text, paste a new text into the Web page, and so on. After you made your changes, you can easily switch back to non-design mode and/or save the modified Web page to HTML file. |
| FavoritesView v1.32 FavoritesView displays the list of all your Favorties (of Internet Explorer browser) and bookmarks (of Netscape/Mozilla browsers) in a single page. Each line in the list specifies the title of the item, the URL address, the created/modified date of the bookmark item, and the folder name. You select one or more of these bookmarks, and then copy them to the clipboard, delete them (Only for Internet Explorer Favorites), export them to tab-delimited text file, HTML file, or XML file. FavoritesView also allows you to locate duplicate URL addresses in your Favorites/Bookmarks or find specific item by specifying the URL or the title. |
| ActiveX Compatibility Manager v1.00 This utility allows you to easily disable/enable ActiveX components on Internet Explorer browser. |
| Video/Audio Related Utilities |
VideoCacheView v3.05 After watching a video in a Web site, you may want to save the video file into your local disk for playing it offline in the future. If the video file is stored in your browser's cache, this utility can help you to extract the video file from the cache and save it for watching it in the future. It automatically scans the entire cache of Internet Explorer and Mozilla-based Web browsers (Including Firefox) and finds all video files that are currently stored in it. It allows you to easily copy the cached video files into another folder for playing/watching them in the future. If you have a movie player that is configured to play flv files, it also allows you to play the video directly from your browser's cache. |
| RTMPDumpHelper v1.22 RTMPDumpHelper is a small utility that can help you to easily download RTMP video/audio streams. By combining this utility and the proxy server of RTMPDump toolkit, you can simply open a Web page containing RTMP video stream in your favorite Web browser, and while watching the video, it'll be saved to your disk automatically as .flv or .mp4 file. RTMP is a streaming protocol used by Hulu, justin.tv, and by many live streaming Web sites. |
SoundVolumeView v2.20 SoundVolumeView is a simple tool for Windows Vista/7/8/2008 that displays general information and current volume level for all active sound components on your system, and allows you to mute and unmute them instantly. SoundVolumeView also allows you to save a sound profile into a file, containing the current volume level and the mute/unmute state of all sound components, as well as the default sound devices, and then later, load the same filename to restore exactly the same volume levels and settings. There is also extensive command-line support, which allows you to save/load profiles, change current volume of every sound component, and mute/unmute every sound component, without displaying any user interface. |
AppAudioConfig v1.15 Starting from Windows Vista, you are allowed to change the sound volume of every application separately, and after you exit from the application, the last settings are saved in the Registry under HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\LowRegistry\Audio\PolicyConfig\PropertyStore so in the next time you run the application, your last settings are used. This tool displays your current audio settings of every application on your system, and allows you to easily change the setting of multiple applications at once. You can change the mute/unmute status, the sound volume level, and the right/left audio balance of the application. |
| Volumouse v2.03 Volumouse provides you a quick and easy way to control the sound volume on your system - simply by rolling the wheel of your wheel mouse. It allows you to define a set of rules for determining when the wheel will be used for changing the sound volume. For example: You can configure Volumouse to use your mouse wheel for volume control when the Alt key is hold down, when the left mouse button is down, when the mouse cursor is over the taskbar, and so on... When the conditions that you define are not satisfied, your mouse wheel will be used for the regular scrolling tasks, exactly as before. |
| InstalledCodec v1.30 InstalledCodec is a small utility displays the list of all Codec drivers and DirectShow filters currently installed on your system. For each component the following information is displayed: Display Name, Type, Disabled Status, Installed/Modified Time, Description, Company Name, Filename, and more... It allows you to easily disable or enable any Codec/DirectShow component or export the list into text/xml/html file. |
| WebVideoCap v1.41 While watching a video in a Web site, you may sometimes want to save the video into your local drive, and then play it offline later. This utility allows you to capture .flv (Flash Video) files and RTSP streams while the Web browser download and play them inside a Web page. After the entire video file is downloaded and played by the Web browser, the video file is saved in the folder that you selected, and you can play it offline later with any Video player. WebVideoCap can capture the video files of most popular video-sharing sites, including YouTube, Google Video, Yahoo Video, iFilm, Metacafe, Putfile, and more... |
| Internet Related Utilities |
| DomainHostingView v1.82 DomainHostingView is a utility for Windows that collects extensive information about a domain by using a series of DNS and WHOIS queries, and generates HTML report that can be displayed in any Web browser. The information displayed by the report of DomainHostingView includes: the hosting company or data center that hosts the Web server, mail server, and domain name server (DNS) of the specified domain, the created/changed/expire date of the domain, domain owner, domain registrar that registered the domain, list of all DNS records, and more... |
| DownTester v1.30 - Internet Speed Test DownTester allows you to easily test your Internet download speed in multiple locations around the world. It automatically test the download speed of the URLs that you choose, one after another. It moves to the next download URL after the specified number of seconds has been elapsed or after it downloads the specified amount of KB - just according to your preferences. After the download test is finished, you can easily save the result into text/html/xml/csv file, or copy it to the clipboard and paste it into Excel and other applications. |
| NetConnectChoose v1.07 NetConnectChoose is a simple tool that allows you to easily choose the default Internet connection that will be used by all Internet applications, when you have more than a single Internet connection on the same time. (Each connection on different network adapter) It also displays extensive information about every active network/Internet connection, including network adapter name, MAC Address, Name Servers, MTU, Interface Speed, current incoming/outgoing data speed, number of received/sent packets, received/sent bytes, and more... |
HostedNetworkStarter v1.15 HostedNetworkStarter is a simple tool for Windows 7 and later that allows you to easily create a wifi hotspot with your wireless network adapter, using the Wifi hosted network feature of Windows operating system. With the wifi hotspot created by this tool, you can allow any device with wifi support to access the network and the Internet connection available in your computer. |
IPNetInfo v1.95 IPNetInfo is a small utility that allows you to easily find all available information about an IP address: The owner of the IP address, the country/state name, IP addresses range, contact information (address, phone, fax, and email), and more. This utility can be very useful for finding the origin of unsolicited mail. You can simply copy the message headers from your email software and paste them into IPNetInfo utility. IPNetInfo automatically extracts all IP addresses from the message headers, and displays the information about these IP addresses. |
| WhoisThisDomain v2.42 This utility allows you to easily get information about a registered domain. It automatically connects to the right WHOIS server, according to the top-level domain name, and retrieve the WHOIS record of the domain. It supports both generic domains and country code domains. |
| IPInfoOffline v1.55 IPInfoOffline Allows you to view information about IP addresses, without connecting any external server. It uses a compressed IP addresses database that is stored inside the exe file. For each IP address, the following information is displayed: IP block range, Organization (RIPE, ARIN, APNIC, LACNIC or AFRINIC), Assigned Date, Country Name, and Country Code. After retrieving the information about the desired IP addresses, You can copy the information to the clipboard, or save it into text/html/xml/csv file. |
| DNSDataView v1.60 This utility is a GUI alternative to the NSLookup tool that comes with Windows operating system. It allows you to easily retrieve the DNS records (MX, NS, A, SOA) of the specified domains. You can use the default DNS server of your Internet connection, or use any other DNS server that you specify. After retrieving the DNS records for the desired domains, you can save them into text/xml/html/csv file. |
| QuickSetDNS v1.30 QuickSetDNS is a simple tool that allows you to easily change the DNS servers that are used for your Internet connection. You can set the desired DNS servers from the user interface, by choosing from a list of DNS servers that you defined, or from command-line, without displaying any user interface. |
| MACAddressView v1.42 MACAddressView is a MAC address lookup tool that allows you to easily find the company details (company name, address, and country) according to the MAC address of a product. MACAddressView also allows you to find MAC address records according to the company name, company address, or country name. After finding the desired MAC address records, you can save them into text/xml/HTML/csv file or copy them to the clipboard and paste them into Excel or other applications. |
| FastResolver v1.26 FastResolver is a small utility that resolves multiple host names into IP addresses and vice versa. You can simply type the list of IP addresses or host name that you want to resolve, or alternatively, you can specify IP addresses range that you want to scan. For local network, FastResolver also allows you to get the MAC address of all IP addresses that you scan. FastResolver is a multithreaded application, so it can resolve dozens of addresses within a few seconds. |
WebSiteSniffer v1.51 WebSiteSniffer is a packet sniffer tool that captures all Web site files downloaded by your Web browser while browsing the Internet, and stores them on your hard drive under the base folder that you choose. WebSiteSniffer allows you to choose which type of Web site files will be captured: HTML Files, Text Files, XML Files, CSS Files, Video/Audio Files, Images, Scripts, and Flash (.swf) files. While capturing the Web site files, the main window of WebSiteSniffer displays general statistics about the downloaded files for every Web site / host name, including the total size of all files (compressed and uncompressed) and total number of files for every file type (HTML, Text, Images, and so on) |
| SiteShoter v1.42 - Capture Website Screenshots SiteShoter is a small utility that allows you to save a screenshot of any Web page into a file. It automatically creates hidden window of Internet Explorer, loads the desired Web page, and than save the entire content of the Web page into an image file (.png, .jpg, .tiff, .bmp or .gif). You can use SiteShoter in user interface mode, or alternatively, you can run SiteShoter in command-line mode without displaying any user interface. |
| SeqDownload v1.26 This utilities allows you to automatically download live images from the Web for every xxx seconds/minutes and store the files on your local drive. After collecting a fair amount of images, you can easily create nice animation from the downloaded images. This utility is especially useful for live cams Web sites, weather radar images, and satellite images. |
| HTMLAsText v1.11 HTMLAsText utility converts HTML documents to simple text files, by removing all HTML tags and formatting the text according to your preferences. |
| AddrView v1.01 AddrView allows you to parse HTML pages and extract most URL addresses stored in them. AddrView extracts URLs of images (<img> tag), links to other files (<a> tag), CSS files, frames, Flash files, and more. |
| TagsReport v1.00 TagsReport reads HTML file and displays statistical information about the tags the appears in it. |
| JavaScript Animator Express v1.10 This utility allows you to easily create animation from image files (GIFs and JPGs) on your local drive. The animation is achieved by creating a simple HTML page with JavaScript animation, and running it on your default browser. |
| CustomizeIE v1.01 Add new menu items and toolbar buttons to Internet Explorer |
| TurnFlash v2.10 (UI Version) TurnFlash is a small utility that allows you to eaily disable and enable the Macromedia Flash player component in Internet Explorer. |
| TurnFlash v1.00 (command-line version) small command-line utility that allows you to eaily disable and enable the Macromedia Flash player component in Internet Explorer. Source code is included ! |
| MIMEView v1.10 This utility displays the list of all MIME types defined in your system. For each MIME type, information about the associated file extension and installed plugin is also displayed. |
| NirCmd v2.86 NirCmd is a small command-line utility that allows you to do some useful tasks without displaying any user interface. By running NirCmd with simple command-line option, you can write and delete values and keys in the Registry, write values into INI file, dial to your internet account or connect to a VPN network, restart windows or shut down the computer, create shortcut to a file, change the created/modified date of a file, change your display settings, and more... |
GetNir v1.00 GetNir is a command-line tool for Windows that receives tab-delimited or comma-delimited data from other NirSoft tools through Standard input (stdin) , finds and extracts the desired values according to the specified filter expression and column names, and then sends these values to the Standard output (stdout). |
| WirelessNetConsole v1.00 WirelessNetConsole is a small console application that dumps all current detected wireless networks information into the standard output. For each wireless network, the following information is displayed: SSID, Signal Quality in %, PHY types, RSSI, MAC Address, Channel Frequency, and more. |
| BluetoothCL v1.07 BluetoothCL is a small console application that dumps all current detected bluetooth devices into the standard output. For each Bluetooth device, the following information is displayed: MAC Address, Name, Major Device Type, Minor Device Type, and optionally the company name of the device (if external file of MAC addresses - oui.txt is provided) |
| RegFileExport v1.11 RegFileExport is a small console application that allows you to easily extract data from offline Registry file located on another disk drive. RegFileExport read the Registry file, ananlyze it, and then export the Registry data into a standard .reg file of Windows. You can export the entire Registry file, or only a specific Registry key. RegFileExport may also be able to export some of the Registry data even when the Registry file is corrupted and cannot be loaded by Windows. |
| RunFromProcess v1.06 RunFromProcess is a command-line utility that allows you to run a program from another process that you choose. The program that you run will be executed as a child of the specified process and it'll run with the same user and security context of the specified parent process. |
| AtNow v1.1 AtNow is a command-line utility that schedules programs and commands to run in the near future. Visual C++ Source code is included. |
| WhosIP v1.18 WhosIP is a simple command-line utility that allows you to easily find all available information about an IP address: The owner of the IP address, the country/state name, IP addresses range, contact information (address, phone, fax, and email), and more. |
| WhoisCL v1.90 WhoisCL is a simple command-line utility that allows you to easily get information about a registered domain. It automatically connect to the right WHOIS server, according to the top-level domain name, and retrieve the WHOIS record of the domain. It supports both generic domains and country code domains. |
| SNRemove v1.00 This utility removes the reference to strong name signature from .NET exe and dll files. After removing the strong name reference, you can make any change you want in dll/exe file, without getting any exception or error message. |
| DumpEDID v1.07 DumpEDID is a small console application that extract the EDID ("Extended display identification data") records from your computer, analyze it, and dump it into the console window. EDID record provide essential information about your monitor: manufacture week/year, monitor manufacturer, monitor model, supported display modes, and so on... You can also get the EDID records of a remote computer, if you login to this computer with administrator rights. (DumpEDID is the console version of MonitorInfoView utility) |
GUIPropView v1.12 GUIPropView displays extensive information about all windows currently opened on your system. The upper pane of GUIPropView displays all top level windows, and when you select a window in the upper pane, the lower pane displays the list of all child windows of the selected top level window. You can also select one or more windows and then do some actions on them like close, hide, show, minimize, maximize, disable, enable, and so on... |
| FileTypesMan v1.95 FileTypesMan is an alternative to the 'File Types' tab in the 'Folder Options' of Windows. It displays the list of all file extensions and types registered on your computer. For each file type, the following information is displayed: Type Name, Description, MIME Type, Perceived Type, Flags, Browser Flags, and more. FileTypesMan also allows you to easily edit the properties and flags of each file type, as well as it allows you to add, edit, and remove actions in a file type. |
| ShortcutsMan v1.10 ShortcutsMan displays the details about all shortcuts that you have on your desktop and under your start menu. Broken shortcuts (shortcuts that point to file that doesn't exist) are automatically painted with pink color. You select one or more shortcuts, and then delete them, resolve them or save the shortcut's details to HTML/Text/XML file. |
| OpenWithView v1.11 OpenWithView is a small utility that displays the list of all available applications in the 'Open With' dialog-box of Windows, and allows you to easily disable/enable the applications in the list. When application is disabled, it won't be displayed in the 'Other Programs' section of the 'Open With' dialog-box. This utility can be useful if your 'Open With' window displays too much applications, and you want to remove the applications that you don't use frequently. |
| SpecialFoldersView v1.26 Windows operating system have dozens of special folders that are used for storing application settings and files, storing Internet files, saving temporary files, storing shortcuts to other files, and so on. This utility displays the list of all special folders in your system, and allows you to easily jump to the right folder simply by double-clicking the folder item. You can also save the list of all folder paths into text/html/xml file. |
| WinLister v1.22 This utility displays the list of opened windows on your system. For each window, some useful information is displayed: the title, the handle of window, location, size, class name, process number, the name of the program that created the window, and more... In addition, you can easily hide, show or close the selected windows, or save the windows list to text or HTML file. |
| InsideClipboard v1.15 Each time that you copy something into the clipboard for pasting it into another application, the copied data is saved into multiple formats. The main clipboard application of Windows only display the basic clipboard formats, like text and bitmaps, but doesn't display the list of all formats that are stored in the clipboard. InsideClipboard is a small utility that displays the binary content of all formats that are currently stored in the clipboard, and allow you to save the content of specific format into a binary file. |
| Clipboardic v1.15 Clipboardic is a small utility that listen to the clipboard activity, and each time that you copy something into the clipboard, it automatically save the copied data into Windows clipboard file (.clp). Later, when you need the copied data again, you can simply select the right clipboard file, and Clipboardic will automatically insert it into the clipboard. Clipboardic also allows you to easily share the clipboard data between multiple computers on your local network. |
| CustomExplorerToolbar v1.05 CustomExplorerToolbar is small utility for Windows 7 only, which allows you to easily customize the toolbar of Windows Explorer, and add buttons that were existed in previous versions of Windows, like Copy, Cut, Paste, Select All, and more. This utility also allows you to remove the toolbar buttons that you previously added. |
| NirExt v1.01 NirExt utility adds 3 useful context menu extensions to your Windows Explorer environment:
|
NK2Edit v3.40 Every time that you type an email address or name in the message window of MS-Outlook, it automatically offer you a list of users and email address that you can choose. This feature is known as 'AutoComplete' and Outlook automatically build this emails list according to user activity and save it into a file with .NK2 extension. In some circumstances, you may need to fix or modify the values appeared in the AutoComplete list, or you may want to remove unwanted email addresses and/or to add new email addresses. MS-Outlook doesn't provide any ability to edit this AutoComplete list, so this is where NK2Edit software can help you. NK2Edit is a real NK2 editor that allows you to modify all fields in NK2 file, delete unwanted records, add new records, repair corrupted nk2 files, merge 2 or more NK2 files into a single NK2 file, and more... |
OutlookAttachView v3.42 OutlookAttachView scans all messages stored in your Outlook, and displays the list of all attached files that it finds. You can easily select one or more attachments and save all of them into the desired folder, as well as you can delete unwanted large attachments that take too much disk space in your mailbox. You can also save the list of attachments into xml/html/text/csv file. |
OutlookStatView v2.18 OutlookStatView scans your Outlook mailbox, and display a general statistics about the users that you communicate via emails. For each user/email, the following information is displayed: The number of outgoing messages that you sent to the user (separated by to/cc/bcc), the number of incoming message that the user sent to you, the total size of messages sent by the user, the email client software used by this user, and the time range that you send/received emails with the specified user. |
OutlookAddressBookView v2.22 OutlookAddressBookView is a simple utility that displays the details of all recipients stored in the address books of Microsoft Outlook. For every recipient entry, the following information is displayed: Email Address, Display Name, Address Type (MS-Exchange or SMTP), Street Address, Phone Number, Created Time, Modified Time (Works only with address books of Exchange server), and more... You can easily select one or more recipients from the list and export them into tab-delimited/comma-delimited/xml/html file, or copy them to the clipboard and then paste the list into Excel. |
| OfficeIns v1.20 - Microsoft Office Add-Ins Manager OfficeIns is a small utility that displays the details of all installed Microsoft Office add-ins on your computer, and allows you to disable/enable them. |
| DLL Export Viewer v1.66 This utility displays the list of all exported functions and their virtual memory addresses for the specified DLL files. You can easily copy the memory address of the desired function, paste it into your debugger, and set a breakpoint for this memory address. When this function is called, the debugger will stop in the beginning of this function. |
| GDIView v1.26 GDIView is a unique tool that displays the list of GDI handles (brushes, pens, fonts, bitmaps, and others) allocated by every process. It displays the total count for each type of GDI handle, as well as detailed information about each handle. This tool can be useful for developers that need to trace GDI resources leak in their software. |
| HeapMemView v1.05 HeapMemView is a small utility that allows you to view the content of all memory blocks allocated in the heap of the process that you select. This tool can be useful for developers that need to trace memory leaks in their software. |
DeviceIOView v1.06 DeviceIOView allows you to watch the data transfer between a software or service and a device driver (DeviceIoControl calls). For each call to a device driver, the following information is displayed: Handle, Control Code, number of input bytes, number of output bytes, the name of the device handle, and all the input/output bytes, displayed as Hex dump. |
| SimpleProgramDebugger v1.10 SimpleProgramDebugger is a simple debugging tool that attaches to existing running program or starts a new program in debugging mode, and then displays all major debugging events occurs while the program is running, including Exception, Create Thread, Create Process, Exit Thread, Exit Process, Load DLL, Unload Dll, and Debug String. After the debugging events are accumulated, you can easily export them into comma-delimited/tab-delimited/xml/html file or copy them to the clipboard and then paste them into Excel or any other spreadsheet application. |
SearchMyFiles v3.10 SearchMyFiles is an alternative to the standard "Search For Files And Folders" module of Windows. It allows you to easily search files in your system by wildcard, by last modified/created/last accessed time, by file attributes, by file content (text or binary search), and by the file size. SearchMyFiles allows you to make a very accurate search that cannot be done with Windows search. For Example: You can search all files created in the last 10 minutes with size between 500 and 700 bytes. After you made a search, you can select one or more files, and save the list into text/html/csv/xml file, or copy the list to the clipboard. |
DriveLetterView v1.50 DriveLetterView is a simple utility that allows you to view the list of all drive letter assignments in your system, including local drives, remote network drives, CD/DVD drives, and USB drives - even if they are not currently plugged. It also allows you to easily change a drive letter of USB devices and remote network shares, as well as to delete a drive letter of USB device that is not plugged. You can also use DriveLetterView to export the list of all drives into text/csv/html/xml file. |
| DiskCountersView v1.27 DiskCountersView displays the system counters of each disk drive in your system, including the total number of read/write operations and the total number of read/write bytes. It also displays general drive information, like disk name, partition number, partition location, and so on. |
AppReadWriteCounter v1.30 AppReadWriteCounter is a tool for Windows that counts and displays the current file read/write operations of every application running on your system. It displays the number of read/write bytes, the number of read/write operations, current calculated read/write speed, and the details about the application (product name, product version, and so on) that makes the file read/write operations. |
FileActivityWatch v1.60 FileActivityWatch is a tool for Windows that displays information about every read/write/delete operation of files occurs on your system. For every file, FileActivityWatch displays the number of read/write bytes, number of read/write/delete operations, first and last read/write timestamp, and the name/ID of the process responsible for the file operation. |
FileAccessErrorView v1.22 FileAccessErrorView is a diagnostic tool for Windows that displays information about errors occur while programs running on your system try to open/read/write/delete a file. FileAccessErrorView displays the filename that the application tried to open/read/write/delete, the process id/name of the application, the error code (NTSTATUS code), the description of the error code, the number of times that this error occurred, and the timestamp of this error. |
| DiskSmartView v1.21 DiskSmartView is a small utility that retrieves the S.M.A.R.T information (S.M.A.R.T = Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) from IDE disks. This information includes the disk model/firmware/serial number, cylinders/heads, power-on hours (POH), internal temperature, disk errors rate, and more. You can use the S.M.A.R.T information retrieved by DiskSmartView to find out whether there is any significant problem in your disk drive. |
| AlternateStreamView v1.56 AlternateStreamView is a small utility that allows you to scan your NTFS drive, and find all hidden alternate streams stored in the file system. After scanning and finding the alternate streams, you can extract these streams into the specified folder, delete unwanted streams, or save the streams list into text/html/csv/xml file. |
| AltStreamDump v1.05 AltStreamDump is a console application (Command Prompt) that dumps the list of NTFS alternate streams found in the current directory. By using a few command-line options, you can also instruct AltStreamDump to displays the alternate streams list of other folders and to scan subfolders in the desired folder depth |
NTFSLinksView v1.32 Starting from Windows Vista, Microsoft uses symbolic links and junction points of NTFS file system in order to make changes in the folders structure of Windows and keep the compatibility of applications written for older versions of Windows. This utility simply shows you to list of all symbolic links and junctions in the specified folder, and their target paths. |
| FoldersReport v1.21 The FoldersReport utility scans a drive or a base folder that you select, and displays essential information for each folder that it finds: The size of all files inside the folder, The real files size on the disk, number of files inside the folder, number of hidden files, number of compressed files, and number of subfolders. You can use this utility to easily find out which folders use the most space in your drive. You can scan the folders of your local drives, CD-ROM drives, and network resources on a remote computer. |
WinUpdatesView v1.13 - Windows Updates History Viewer WinUpdatesView is a simple tool that displays the history of Windows updates on your system. WinUpdatesView can load the Windows updates history from your local system, using API, and it can also read and parse the Windows updates database file (DataStore.edb) from external drive or from remote computer on your network. For every Windows update history record, WinUpdatesView displays the following fields: Title, Description, Install Date, Update Operation (Install, Uninstall, Not Started, In Progress), Operation Result (Succeeded, Succeeded With Errors, Failed, Aborted), Category, Information URL, Support URL, Uninstall Notes, Client Application ID, Service ID, Update ID, Revision Number, Unmapped Result Code, Server Selection, hResult |
MultiMonitorTool v1.96 MultiMonitorTool is a small tool that allows you to do some actions related to working with multiple monitors. With MultiMonitorTool, you can disable/enable monitors, set the primary monitor, save and load the configuration of all monitors, and move windows from one monitor to another. You can do these actions from the user interface or from command-line, without displaying user interface. MultiMonitorTool also provides a preview window, which allows you to watch a preview of every monitor on your system. |
| ControlMyMonitor v1.26 ControlMyMonitor allows you view and modify the settings of your monitor (Also known as 'VCP Features'), like brightness, contrast, sharpness, red/green/blue color balance, and more... You can modify the monitor settings from the GUI and from command-line. You can also export all settings of your monitor into a configuration file and then later load the same configuration back into your monitor. |
| PropertySystemView v1.13 PropertySystemView is a tool that allows you view and modify the properties of file from GUI and command-line, using the property system of Windows operating system. For example, you can change the 'Media Created' timestamp stored in .mp4 files (System.Media.DateEncoded) as well as other metadata stored in media files and office documents, like Title, Comments, Authors, Tags, Date Acquired, Last Saved Date, Content Created Date, Date Imported, Date Taken (EXIF of .jpg files), and more... PropertySystemView also allows you to set properties of Windows. For example, you can set the System.AppUserModel.ID property of a window in order to disable the taskbar grouping of the specified window. |
BlueScreenView v1.55 BlueScreenView scans all your minidump files created during 'blue screen of death' crashes, and displays the information about all crashes in one table. For each crash, BlueScreenView displays the minidump filename, the date/time of the crash, the basic crash information displayed in the blue screen (Bug Check Code and 4 parameters), and the details of the driver or module that possibly caused the crash (filename, product name, file description, and file version). For each crash displayed in the upper pane, you can view the details of the device drivers loaded during the crash in the lower pane. BlueScreenView also mark the drivers that their addresses found in the crash stack, so you can easily locate the suspected drivers that possibly caused the crash. |
USBDeview v3.01 USBDeview is a small utility that lists all USB devices that currently connected to your computer, as well as all USB devices that you previously used. For each USB device, extended information is displayed: Device name/description, device type, serial number (for mass storage devices), the date/time that device was added, VendorID, ProductID, and more... USBDeview also allows you to uninstall USB devices that you previously used, and disconnect USB devices that are currently connected to your computer. You can also use USBDeview on a remote computer, as long as you login to that computer with admin user. |
USBLogView v1.26 USBLogView is a small utility that runs in the background and records the details of any USB device that is plugged or unplugged into your system. For every log line created by USBLogView, the following information is displayed: Event Type (Plug/Unplug), Event Time, Device Name, Description, Device Type, Drive Letter (For storage devices), Serial Number (Only for some types of devices), Vendor ID, Product ID, Vendor Name, Product Name, and more... You can easily select one or more log records and then export them into csv/tab-delimited/xml/html file. |
UninstallView v1.38 UninstallView is a tool for Windows that collects information about all programs installed on your system and displays the details of the installed programs in one table. You can use it to get installed programs information for your local system, for remote computer on your network, and for external hard-drive plugged to your computer. It also allows you to easily uninstall a software on your local computer and remote computer (Including quiet uninstall if the installer supports it). |
InstalledAppView v1.01 InstalledAppView is a tool for Windows 10 that displays the details of Windows 10 apps installed on your system. For every Windows app, the following information is displayed: App Name, App Version, Registry Name, Registry Modified Time, Install Folder, Install Folder Owner, Uninstall Command, and more... InstalledAppView allows you to load the Windows 10 apps list from your local system, remote computer on your network and from external disk plugged to your computer. InstalledAppView also allows you to view the XML files of the Windows app (AppxManifest.xml and AppxBlockMap.xml), uninstall apps, quietly uninstall apps, open the install folder of the app, and more... |
| InstalledPackagesView v1.05 InstalledPackagesView is a tool for Windows that displays the list of all software packages installed on your system with Windows Installer, and lists the files, Registry keys, and .NET Assemblies associated with them. For every installed software, the following information is displayed: Display Name, Display Version, Install Date, Registry Time, Estimated Size, Install Location, Install Source, MSI Filename (In C:\Windows\Installer), and more... You can watch the installed software packages information from your local system or from another system on external hard-drive. |
| RegistryChangesView v1.26 RegistryChangesView is a tool for Windows that allows you to take a snapshot of Windows Registry and later compare it with another Registry snapshots, with the current Registry or with Registry files stored in a shadow copy created by Windows. When comparing 2 Registry snapshots, you can see the exact changes made in the Registry between the 2 snapshots, and optionally export the Registry changes into a standard .reg file of RegEdit. |
WinDefThreatsView v1.06 WinDefThreatsView is tool for Windows 10 that displays the list of all threats detected by Windows Defender Antivirus and allows you to easily set the default action (Allow, Quarantine, Clean, Remove, Block, or No Action) for multiple threats at once. You can use this tool on your local computer and also on remote computer, as long as you have permission to access WMI on the remote machine. |
WinCrashReport v1.25 WinCrashReport provides an alternative to the built-in crash reporting program of Windows operating system. When application crashes in your system and Windows displays the internal crash window of the operating system, you can run WinCrashReport, and get extensive report about the crashed application. The crash report of WinCrashReport is displayed as simple text or in HTML, and includes the following information: Crash memory address, Exception code, Exception description, Strings found in the stack, call stack, processor registers, modules list, threads list, and more... |
WhatIsHang v1.27 |
Windows Vista
| A version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 | |
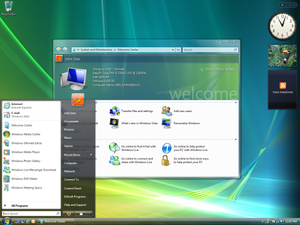 | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model | |
| Released to manufacturing | November 8, 2006; 13 years ago (2006-11-08)[2] |
| General availability | January 30, 2007; 13 years ago (2007-01-30)[3] |
| Final release | Service Pack 2 (6.0.6002)[4] / May 26, 2009; 11 years ago (2009-05-26)[5] |
| Update method | |
| Platforms | IA-32 and x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| License | Proprietarycommercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows XP (2001) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 7 (2009) |
| Official website | www.microsoft.com/windows/windows-vista/default.aspx |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on April 10, 2012 Extended support ended on April 11, 2017[6] | |
Windows Vista is an operating system produced by Microsoft as a member of the Windows NT family of operating systems for use on personal computers. Development was completed on November 8, 2006,[2] and over the following three months, it was released in stages to computer hardware and software manufacturers, business customers and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released worldwide[3] and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.[7] The release of Windows Vista came more than five years after the introduction of its predecessor, Windows XP, the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows desktop operating systems.
New features of Windows Vista include an updated graphical user interface and visual style dubbed Aero, a new search component called Windows Search, redesigned networking, audio, print and display sub-systems, and new multimedia tools such as Windows DVD Maker. Vista aimed to increase the level of communication between machines on a home network, using peer-to-peer technology to simplify sharing files and media between computers and devices. Windows Vista included version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs.
Microsoft's primary stated objective with Windows Vista was to improve the state of security in the Windows operating system.[8] One common criticism of Windows XP and its predecessors was their commonly exploited security vulnerabilities and overall susceptibility to malware, viruses and buffer overflows. In light of this, Microsoft chairman Bill Gates announced in early 2002 a company-wide "Trustworthy Computing initiative", which aimed to incorporate security into every aspect of software development at the company.[9] Microsoft stated that it prioritized improving the security of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 above finishing Windows Vista, thus delaying its completion.[10][11]
While these new features and security improvements garnered positive reviews, Vista was also the target of much criticism and negative press. Criticism of Windows Vista targeted its high system requirements, its more restrictive licensing terms, the inclusion of a number of then-new DRM technologies aimed at restricting the copying of protected digital media, lack of compatibility with some pre-Vista hardware and software, longer boot time, and the number of authorization prompts for User Account Control. As a result of these and other issues, Windows Vista saw initial adoption and satisfaction rates lower than Windows XP.[12] However, Vista usage had surpassed Microsoft's pre-launch two-year-out expectations of achieving 200 million users, with an estimated 330 million Internet users in January 2009.[13][14]
At the release of its successor, Windows 7 (October 2009), Windows Vista (with approximately 400 million Internet users) was the second most widely used operating system on the Internet with an approximately 19% market share, the most widely used being Windows XP with an approximately 63% market share.[15] In May 2010, Windows Vista's market share had an estimated range from 15% to 26%.[16][17] On October 22, 2010, Microsoft ceased sales of retail copies of Windows Vista, and the OEM sales for Vista ceased a year later.[18]
Mainstream support for Vista ended on April 10, 2012,[19] and extended support ended on April 11, 2017.[20] As of August 2020[update], Vista's market share has declined to 0.42% of Windows' total market share (0.32% of all traditional PCs).[21]
Development[edit]
Microsoft began work on Windows Vista, known at the time by its codename "Longhorn", in May 2001,[22] five months before the release of Windows XP. It was originally expected to ship in late 2003 as a minor step between Windows XP and "Blackcomb", which was planned to be the company's next major operating system release (which would eventually be released as Windows 7). Gradually, "Longhorn" assimilated many of the important new features and technologies slated for Blackcomb, resulting in the release date being pushed back several times in three years. In some builds of Longhorn, their license agreement said "For the Microsoft product codenamed 'Whistler'". Many of Microsoft's developers were also re-tasked to build updates to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to strengthen security. Faced with ongoing delays and concerns about feature creep, Microsoft announced on August 27, 2004, that it had revised its plans. For this reason, Longhorn was reset to start work on componentizing the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 codebase, and over time re-incorporating the features that would be intended for an actual operating system release. However, some previously announced features such as WinFS were dropped or postponed, and a new software development methodology called the Security Development Lifecycle was incorporated to address concerns with the security of the Windows codebase, which is programmed in C, C++ and assembly. Longhorn became known as Vista in 2005.[23][24]
As Longhorn[edit]
The early development stages of Longhorn were generally characterized by incremental improvements and updates to Windows XP. During this period, Microsoft was fairly quiet about what was being worked on, as their marketing and public relations efforts were more strongly focused on Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, which was released in April 2003. Occasional builds of Longhorn were leaked onto popular file sharing networks such as IRC, BitTorrent, eDonkey and various newsgroups, and so most of what is known about builds before the first sanctioned development release of Longhorn in May 2003 is derived from these builds.
After several months of relatively little news or activity from Microsoft with Longhorn, Microsoft released Build 4008, which had made an appearance on the Internet around February 28, 2003.[25] It was also privately handed out to a select group of software developers. As an evolutionary release over build 3683, it contained several small improvements, including a modified blue "Plex" theme and a new, simplified Windows Image-based installer that operates in graphical mode from the outset, and completed an install of the operating system in approximately one third the time of Windows XP on the same hardware. An optional "new taskbar" was introduced that was thinner than the previous build and displayed the time differently.
The most notable visual and functional difference, however, came with Windows Explorer. The incorporation of the Plex theme made blue the dominant color of the entire application. The Windows XP-style task pane was almost completely replaced with a large horizontal pane that appeared under the toolbars. A new search interface allowed for filtering of results, searching for Windows help, and natural-language queries that would be used to integrate with WinFS. The animated search characters were also removed. The "view modes" were also replaced with a single slider that would resize the icons in real-time, in the list, thumbnail, or details mode, depending on where the slider was. File metadata was also made more visible and more easily editable, with more active encouragement to fill out missing pieces of information. Also of note was the conversion of Windows Explorer to being a .NET application.
Most builds of Longhorn and Vista were identified by a label that was always displayed in the bottom-right corner of the desktop. A typical build label would look like "Longhorn Build 3663.Lab06_N.020728-1728". Higher build numbers did not automatically mean that the latest features from every development team at Microsoft was included. Typically, a team working on a certain feature or subsystem would generate their working builds which developers would test with, and when the code was deemed stable, all the changes would be incorporated back into the main development tree at once. At Microsoft, several "Build labs" exist where the compilation of the entirety of Windows can be performed by a team. The name of the lab in which any given build originated is shown as part of the build label, and the date and time of the build follow that. Some builds (such as Beta 1 and Beta 2) only display the build label in the version information dialog (Winver). The icons used in these builds are from Windows XP.
At the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference (WinHEC) in May 2003, Microsoft gave their first public demonstrations of the new Desktop Window Manager and Aero. The demonstrations were done on a revised build 4015 which was never released. Several sessions for developers and hardware engineers at the conference focused on these new features, as well as the Next-Generation Secure Computing Base (previously known as "Palladium"), which at the time was Microsoft's proposed solution for creating a secure computing environment whereby any given component of the system could be deemed "trusted". Also at this conference, Microsoft reiterated their roadmap for delivering Longhorn, pointing to an "early 2005" release date.[26]
Development reset[edit]
By 2004, it had become obvious to the Windows team at Microsoft that they were losing sight of what needed to be done to complete the next version of Windows and ship it to customers. Internally, some Microsoft employees were describing the Longhorn project as "another Cairo" or "Cairo.NET", referring to the Cairo development project that the company embarked on through the first half of the 1990s, which never resulted in a shipping operating system (though nearly all the technologies developed in that time did end up in Windows 95 and Windows NT[27]). Microsoft was shocked in 2005 by Apple's release of Mac OS X Tiger. It offered only a limited subset of features planned for Longhorn, in particular fast file searching and integrated graphics and sound processing, but appeared to have impressive reliability and performance compared to contemporary Longhorn builds.[28] Most Longhorn builds had major Explorer.exe system leaks which prevented the OS from performing well, and added more confusion to the development teams in later builds with more and more code being developed which failed to reach stability.
In a September 23, 2005 front-page article in The Wall Street Journal,[29] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin, who had overall responsibility for the development and delivery of Windows, explained how development of Longhorn had been "crashing into the ground" due in large part to the haphazard methods by which features were introduced and integrated into the core of the operating system, without a clear focus on an end-product. Allchin went on to explain how in December 2003, he enlisted the help of two other senior executives, Brian Valentine and Amitabh Srivastava, the former being experienced with shipping software at Microsoft, most notably Windows Server 2003,[30] and the latter having spent his career at Microsoft researching and developing methods of producing high-quality testing systems.[31] Srivastava employed a team of core architects to visually map out the entirety of the Windows operating system, and to proactively work towards a development process that would enforce high levels of code quality, reduce interdependencies between components, and in general, "not make things worse with Vista".[32] Since Microsoft decided that Longhorn needed to be further componentized, work started on the Omega-13 series builds where they would componentize existing Windows Server 2003 source code, and over time add back functionality as development progressed. Future Longhorn builds would start from Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 and continue from there.
This change, announced internally to Microsoft employees on August 26, 2004, began in earnest in September, though it would take several more months before the new development process and build methodology would be used by all of the development teams. A number of complaints came from individual developers, and Bill Gates himself, that the new development process was going to be prohibitively difficult to work within.
As Windows Vista[edit]
By approximately November 2004, the company had considered several names for the final release, ranging from simple to fanciful and inventive. In the end, Microsoft chose Windows Vista as confirmed on July 22, 2005, believing it to be a "wonderful intersection of what the product really does, what Windows stands for, and what resonates with customers, and their needs". Group Project Manager Greg Sullivan told Paul Thurrott "You want the PC to adapt to you and help you cut through the clutter to focus on what's important to you. That's what Windows Vista is all about: "bringing clarity to your world" (a reference to the three marketing points of Vista—Clear, Connected, Confident), so you can focus on what matters to you".[33] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin also loved the name, saying that "Vista creates the right imagery for the new product capabilities and inspires the imagination with all the possibilities of what can be done with Windows—making people's passions come alive."[34]
After Longhorn was named Windows Vista in July 2005, an unprecedented beta-test program was started, involving hundreds of thousands of volunteers and companies. In September of that year, Microsoft started releasing regular Community Technology Previews (CTP) to beta testers from July 2005 to February 2006. The first of these was distributed at the 2005 Microsoft Professional Developers Conference, and was subsequently released to beta testers and Microsoft Developer Network subscribers. The builds that followed incorporated most of the planned features for the final product, as well as a number of changes to the user interface, based largely on feedback from beta testers. Windows Vista was deemed feature-complete with the release of the "February CTP", released on February 22, 2006, and much of the remainder of the work between that build and the final release of the product focused on stability, performance, application and driver compatibility, and documentation. Beta 2, released in late May, was the first build to be made available to the general public through Microsoft's Customer Preview Program. It was downloaded over 5 million times. Two release candidates followed in September and October, both of which were made available to a large number of users.[35]
At the Intel Developer Forum on March 9, 2006, Microsoft announced a change in their plans to support EFI in Windows Vista. The UEFI 2.0 specification (which replaced EFI 1.10) was not completed until early 2006, and at the time of Microsoft's announcement, no firmware manufacturers had completed a production implementation which could be used for testing. As a result, the decision was made to postpone the introduction of UEFI support to Windows; support for UEFI on 64-bit platforms was postponed until Vista Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 and 32-bit UEFI would not be supported, as Microsoft did not expect many such systems to be built because the market was quickly moving to 64-bit processors.[36][37]
While Microsoft had originally hoped to have the consumer versions of the operating system available worldwide in time for the 2006 holiday shopping season, it announced in March 2006 that the release date would be pushed back to January 2007 in order to give the company—and the hardware and software companies that Microsoft depends on for providing device drivers—additional time to prepare. Because a release to manufacturing (RTM) build is the final version of code shipped to retailers and other distributors, the purpose of a pre-RTM build is to eliminate any last "show-stopper" bugs that may prevent the code from responsibly being shipped to customers, as well as anything else that consumers may find annoying. Thus, it is unlikely that any major new features would be introduced; instead, work would focus on Vista's fit and finish. In just a few days, developers had managed to drop Vista's bug count from over 2470 on September 22 to just over 1400 by the time RC2 shipped in early October. However, they still had a way to go before Vista was ready to RTM. Microsoft's internal processes required Vista's bug count to drop to 500 or fewer before the product could go into escrow for RTM.[38] For most of the pre-RTM builds, those 32-bit editions are only released.
On June 14, 2006, Windows developer Philip Su posted a blog entry which decried the development process of Windows Vista, stating that "The code is way too complicated, and that the pace of coding has been tremendously slowed down by overbearing process."[39] The same post also described Windows Vista as having approximately 50 million lines of code, with about 2,000 developers working on the product. During a demonstration of the speech recognition feature new to Windows Vista at Microsoft's Financial Analyst Meeting on July 27, 2006, the software recognized the phrase "Dear mom" as "Dear aunt". After several failed attempts to correct the error, the sentence eventually became "Dear aunt, let's set so double the killer delete select all".[40] A developer with Vista's speech recognition team later explained that there was a bug with the build of Vista that was causing the microphone gain level to be set very high, resulting in the audio being received by the speech recognition software being "incredibly distorted".[41]
Windows Vista build 5824 (October 17, 2006) was supposed to be the RTM release, but a bug, which destroyed any system that was upgraded from Windows XP, prevented this, damaging development and lowering the chance that it would hit its January 2007 deadline.[42]
Development of Windows Vista came to an end when Microsoft announced that it had been finalized on November 8, 2006, and was concluded by co-president of Windows development, Jim Allchin.[43] The RTM's build number had also jumped to 6000 to reflect Vista's internal version number, NT 6.0.[44] Jumping RTM build numbers is common practice among consumer-oriented Windows versions, like Windows 98 (build 1998), Windows 98 SE (build 2222), Windows Me (build 3000) or Windows XP (build 2600), as compared to the business-oriented versions like Windows 2000 (build 2195) or Server 2003 (build 3790). On November 16, 2006, Microsoft made the final build available to MSDN and Technet Plus subscribers.[45] A business-oriented Enterprise edition was made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006.[46] Windows Vista was launched for general customer availability on January 30, 2007.
New or changed features[edit]
Windows Vista introduced several features and functionality not present in its predecessors.
End-user[edit]
- Windows Aero: The new graphical user interface is named Windows Aero, which Jim Allchin stated is an acronym for Authentic, Energetic, Reflective, and Open.[47] Microsoft intended the new interface to be cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing than those of previous Windows versions, featuring new transparencies, live thumbnails, live icons, and animations, thus providing a new level of eye candy. Laptop users report, however, that enabling Aero shortens battery life[48][49] and reduces performance.
- Windows shell: The new Windows shell offers a new range of organization, navigation, and search capabilities: Task panes in Windows Explorer are removed, integrating the relevant task options into the toolbar. A "Favorite links" pane has been added, enabling one-click access to common directories. A search box appears in every Explorer window. The address bar has been replaced with a breadcrumb navigation bar. Icons of certain file types in Windows Explorer are "live" and can be scaled in size up to 256 × 256 pixels. The preview pane allows users to see thumbnails of various files and view the contents of documents. The details pane shows information such as file size and type, and allows viewing and editing of embedded tags in supported file formats. The Start menu has changed as well; incorporating an instant search box, and the All Programs list uses a horizontal scroll bar instead of the cascading flyout menu seen in Windows XP. The word "Start" itself has been removed in favor of a blue orb that bears the Windows logo.
- Windows Search: A new search component of Windows Vista, it features instant search (also known as search as you type), which provides instant search results, thus finding files more quickly than the search features found in previous versions of Windows and can search the contents of recognized file types.[50] Users can search for certain metadata such as name, extension, size, date or attributes.
- Windows Sidebar: A transparent panel, anchored to the right side of the screen, wherein a user can place Desktop Gadgets, which are small applets designed for a specialized purpose (such as displaying the weather or sports scores). Gadgets can also be placed on the desktop.[51]
- Windows Internet Explorer 7: New user interface, tabbed browsing, RSS, a search box, improved printing,[52] Page Zoom, Quick Tabs (thumbnails of all open tabs), Anti-Phishing filter, a number of new security protection features, Internationalized Domain Name support (IDN), and improved web standards support. IE7 in Windows Vista runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system (protected mode); exploits and malicious software are restricted from writing to any location beyond Temporary Internet Files without explicit user consent.
- Windows Media Player 11, a major revamp of Microsoft's program for playing and organizing music and video. New features in this version include word wheeling (incremental search or "search as you type"), a new GUI for the media library, photo display and organization, the ability to share music libraries over a network with other Windows Vista machines, Xbox 360 integration, and support for other Media Center Extenders.
- Windows Defender: An antispyware program with several real-time protection agents. It includes a software explorer feature, which provides access to startup programs, and allows one to view currently running software, network connected applications, and Winsock providers (Winsock LSPs).
- Backup and Restore Center: Includes a backup and restore application that gives users the ability to schedule periodic backups of files on their computer, as well as recovery from previous backups. Backups are incremental, storing only the changes made each time, minimizing disk usage. It also features Complete PC Backup (available only in the Ultimate, Business, and Enterprise editions), which backs up an entire computer as an image onto a hard disk or DVD. Complete PC Backup can automatically recreate a machine setup onto new hardware or hard disk in case of any hardware failures. Complete PC Restore can be initiated from within Windows Vista or from the Windows Vista installation CD in the event that a PC is so corrupt that it cannot start normally from the hard disk.
- Windows Mail: A replacement for Outlook Express that includes a new mail store that improves stability,[53] and features integrated instant search. It has the Phishing Filter like Internet Explorer 7 and Junk mail filtering that is enhanced through regular updates via Windows Update.[54]
- Windows Calendar is a new calendar and task application which integrates with Windows Contacts and Windows Mail. It is compatible with various calendar file types, such as the popular iCalendar.
- Windows Photo Gallery, a photo and movie library management application. It can import from digital cameras, tag and rate individual items, adjust colors and exposure, create and display slideshows (with pan and fade effects) through Direct3D and burn slideshows to a DVD.
- Windows DVD Maker, a companion program to Windows Movie Maker that provides the ability to create video DVDs based on a user's content. Users can design a DVD with title, menus, video, soundtrack, pan and zoom motion effects on pictures or slides.
- Windows Media Center, which was previously exclusively bundled in a separate edition of Windows XP, known as Windows XP Media Center Edition, has been incorporated into the Home Premium and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista.
- Games: Most of the standard computer games included in previous versions of Windows have been redesigned to showcase Vista's new graphical capabilities. New games available in Windows Vista are Chess Titans (3D Chess game), Mahjong Titans (3D Mahjong game), and Purble Place (a small collection of games, oriented towards younger children, including a matching game, a cake-creator game, and a dress-up puzzle game). Purble Place is the only one of the new games available in the Windows Vista Home Basic edition. InkBall is available for Home Premium (or better) users.
- Games Explorer: A new special folder called "Games" exposes installed video games and information about them. These metadata may be updated from the Internet.[55]
- Windows Mobility Center is a control panel that centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing (brightness, sound, battery level / power scheme selection, wireless network, screen orientation, presentation settings, etc.).
- Windows Fax and Scan Allows computers with fax modems to send and receive fax documents, as well as scan documents. It is not available in the Home editions of Windows Vista, but is available in the Business, Enterprise and Ultimate editions.
- Windows Meeting Space replaces NetMeeting. Users can share applications (or their entire desktop) with other users on the local network, or over the Internet using peer-to-peer technology (higher editions than Starter and Home Basic can take advantage of hosting capabilities, Starter and Home Basic editions are limited to "join" mode only)
- Windows HotStart enables compatible computers to start applications directly from operating system startup or resume by the press of a button—this enables what Microsoft has described as appliance-like availability, which allows computers to function in a manner similar to a consumer electronics device such as a DVD player;[56] the feature was also designed to provide the instant-on feature availability that is traditionally associated with mobile devices.[57] While Microsoft has emphasized multimedia scenarios with Windows HotStart,[58] a user can configure this feature so that a button launches a preferred application.[59]
- Shadow Copy automatically creates daily backup copies of files and folders. Users can also create "shadow copies" by setting a System Protection Point using the System Protection tab in the System control panel. The user can view multiple versions of a file throughout a limited history and be allowed to restore, delete, or copy those versions. This feature is available only in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista and is inherited from Windows Server 2003.[60]
- Windows Update: Software and security updates have been simplified,[61] now operating solely via a control panel instead of as a web application. Windows Mail's spam filter and Windows Defender's definitions are updated automatically via Windows Update. Users who choose the recommended setting for Automatic Updates will have the latest drivers installed and available when they add a new device.
- Parental controls: Allows administrators to monitor and restrict user activity, as well as control which websites, programs and games each Standard user can use and install. This feature is not included in the Business or Enterprise editions of Vista.
- Windows SideShow: Enables the auxiliary displays on newer laptops or on supported Windows Mobile devices. It is meant to be used to display device gadgets while the computer is on or off.
- Speech recognition is integrated into Vista.[62] It features a redesigned user interface and configurable command-and-control commands. Unlike the Office 2003 version, which works only in Office and WordPad, Speech Recognition in Windows Vista works for any accessible application. In addition, it currently supports several languages: British and American English, Spanish, French, German, Chinese (Traditional and Simplified) and Japanese.
- New fonts, including several designed for screen reading, and improved Chinese (Yahei, JhengHei), Japanese (Meiryo), and Korean (Malgun) fonts. ClearType has also been enhanced and enabled by default.
- Improved audio controls allow the system-wide volume or volume of individual audio devices and even individual applications to be controlled separately. New audio functionalities such as room correction, bass management, speaker fill, and headphone virtualization have also been incorporated.
- Problem Reports and Solutions, a feature that allows users to check for solutions to problems or view previously sent problems for any solutions or additional information, if available.
- Windows System Assessment Tool is a tool used to benchmark system performance. Software such as games can retrieve this rating and modify its own behavior at runtime to improve performance. The benchmark tests CPU, RAM, 2-D and 3-D graphics acceleration, graphics memory and hard disk space.[63][64]
- Windows Ultimate Extras: The Ultimate edition of Windows Vista provides, via Windows Update, access to some additional features. These are a collection of additional MUI language packs, Texas Hold 'Em (a Poker game) and Microsoft Tinker (a strategy game where the character is a robot), BitLocker and EFS enhancements that allow users to back up their encryption key online in a Digital Locker, and Windows Dreamscene, which enables the use of videos in MPEG and WMV formats as the desktop background. On April 21, 2008, Microsoft launched two more Ultimate Extras; three new Windows sound schemes, and a content pack for Dreamscene. Various DreamScene Content Packs have been released since the final version of DreamScene was released.
- Reliability and Performance Monitor includes various tools for tuning and monitoring system performance and resources activities of CPU, disks, network, memory and other resources. It shows the operations on files, the opened connections, etc.[65]
- Disk Management: The Logical Disk Manager in Windows Vista supports shrinking and expanding volumes on-the-fly.[66]
- Windows Anytime Upgrade: is a program that allows a user to upgrade their computer running Vista to a higher edition. For example, a computer running Windows Vista Home Basic can be upgraded to Home Premium or better. Anytime Upgrade permits users to upgrade without having their programs and data erased, and is cheaper than replacing the existing installation of Windows. Anytime Upgrade is no longer available for Vista.[67]
- Digital Locker Assistant: A program that facilitated access to downloads and purchases from the Windows Marketplacedigital distribution platform.[68] Apps purchased from Windows Marketplace are managed by Microsoft Account credentials, which are used to access a user's digital locker that stores the app and its associated information (e.g., licenses) off-site.[69]
Core[edit]
Vista includes technologies such as ReadyBoost[70] and ReadyDrive, which employ fast flash memory (located on USB flash drives and hybrid hard disk drives) to improve system performance by caching commonly used programs and data. This manifests itself in improved battery life on notebook computers as well, since a hybrid drive can be spun down when not in use.[71] Another new technology called SuperFetch utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze usage patterns to allow Windows Vista to make intelligent decisions about what content should be present in system memory at any given time. It uses almost all the extra RAM as disk cache.[72] In conjunction with SuperFetch, an automatic built-in Windows Disk Defragmenter makes sure that those applications are strategically positioned on the hard disk where they can be loaded into memory very quickly with the least amount of physical movement of the hard disk's read-write heads.[73]
As part of the redesign of the networking architecture, IPv6 has been fully incorporated into the operating system[74] and a number of performance improvements have been introduced, such as TCP window scaling.[75] Earlier versions of Windows typically needed third-party wireless networking software to work properly, but this is not the case with Vista, which includes more comprehensive wireless networking support.[76]
For graphics, Vista introduces a new Windows Display Driver Model[77] and a major revision to Direct3D. The new driver model facilitates the new Desktop Window Manager, which provides the tearing-free desktop and special effects that are the cornerstones of Windows Aero. Direct3D 10, developed in conjunction with major graphics card manufacturers, is a new architecture with more advanced shader support, and allows the graphics processing unit to render more complex scenes without assistance from the CPU. It features improved load balancing between CPU and GPU and also optimizes data transfer between them.[78] WDDM also provides video content playback that rivals typical consumer electronics devices. It does this by making it easy to connect to external monitors, providing for protected HD video playback and increasing overall video playback quality. For the first time in Windows, graphics processing unit (GPU) multitasking is possible, enabling users to run more than one GPU-intensive application simultaneously.[79]
At the core of the operating system, many improvements have been made to the memory manager, process scheduler and I/O scheduler. The Heap Manager implements additional features such as integrity checking in order to improve robustness and defend against buffer overflow security exploits, although this comes at the price of breaking backward compatibility with some legacy applications.[80] A Kernel Transaction Manager has been implemented that enables applications to work with the file system and Registry using atomic transaction operations.[81]
Security-related[edit]
Improved security was a primary design goal for Vista.[8] Microsoft's Trustworthy Computing initiative, which aims to improve public trust in its products, has had a direct effect on its development. This effort has resulted in a number of new security and safety features and an Evaluation Assurance Level rating of 4+.[82][83]
User Account Control, or UAC is perhaps the most significant and visible of these changes. UAC is a security technology that makes it possible for users to use their computer with fewer privileges by default, with a view to stopping malware from making unauthorized changes to the system. This was often difficult in previous versions of Windows, as the previous "limited" user accounts proved too restrictive and incompatible with a large proportion of application software, and even prevented some basic operations such as looking at the calendar from the notification tray. In Windows Vista, when an action is performed that requires administrative rights (such as installing/uninstalling software or making system-wide configuration changes), the user is first prompted for an administrator name and password; in cases where the user is already an administrator, the user is still prompted to confirm the pending privileged action. Regular use of the computer such as running programs, printing, or surfing the Internet does not trigger UAC prompts. User Account Control asks for credentials in a Secure Desktop mode, in which the entire screen is dimmed, and only the authorization window is active and highlighted. The intent is to stop a malicious program misleading the user by interfering with the authorization window, and to hint to the user the importance of the prompt.[84]
Testing by Symantec Corporation has proven the effectiveness of UAC. Symantec used over 2,000 active malware samples, consisting of backdoors, keyloggers, rootkits, mass mailers, trojan horses, spyware, adware, and various other samples. Each was executed on a default Windows Vista installation within a standard user account. UAC effectively blocked over 50 percent of each threat, excluding rootkits. 5 percent or less of the malware that evaded UAC survived a reboot.[85][86]
Internet Explorer 7's new security and safety features include a phishing filter, IDN with anti-spoofing capabilities, and integration with system-wide parental controls. For added security, ActiveX controls are disabled by default. Also, Internet Explorer operates in a protected mode, which operates with lower permissions than the user and runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system, preventing it from accessing or modifying anything besides the Temporary Internet Files directory.[87] Microsoft's anti-spyware product, Windows Defender, has been incorporated into Windows, providing protection against malware and other threats. Changes to various system configuration settings (such as new auto-starting applications) are blocked unless the user gives consent.
Whereas prior releases of Windows supported per-file encryption using Encrypting File System, the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista include BitLocker Drive Encryption, which can protect entire volumes, notably the operating system volume. However, BitLocker requires approximately a 1.5-gigabyte partition to be permanently not encrypted and to contain system files in order for Windows to boot. In normal circumstances, the only time this partition is accessed is when the computer is booting, or when there is a Windows update that changes files in this area, which is a legitimate reason to access this section of the drive. The area can be a potential security issue, because a hexadecimal editor (such as dskprobe.exe), or malicious software running with administrator and/or kernel level privileges would be able to write to this "Ghost Partition" and allow a piece of malicious software to compromise the system, or disable the encryption. BitLocker can work in conjunction with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) cryptoprocessor (version 1.2) embedded in a computer's motherboard, or with a USB key.[88] However, as with other full disk encryption technologies, BitLocker is vulnerable to a cold boot attack, especially where TPM is used as a key protector without a boot PIN being required too.[89]
A variety of other privilege-restriction techniques are also built into Vista. An example is the concept of "integrity levels" in user processes, whereby a process with a lower integrity level cannot interact with processes of a higher integrity level and cannot perform DLL–injection to a processes of a higher integrity level. The security restrictions of Windows services are more fine-grained, so that services (especially those listening on the network) have no ability to interact with parts of the operating system they do not need to. Obfuscation techniques such as address space layout randomization are used to increase the amount of effort required of malware before successful infiltration of a system. Code integrity verifies that system binaries have not been tampered with by malicious code.
As part of the redesign of the network stack, Windows Firewall has been upgraded, with new support for filtering both incoming and outgoing traffic. Advanced packet filter rules can be created that can grant or deny communications to specific services.
The 64-bit versions of Vista require that all device drivers be digitally signed, so that the creator of the driver can be identified.[90]
System management[edit]
While much of the focus of Vista's new capabilities highlighted the new user-interface,[91] security technologies, and improvements to the core operating system, Microsoft also adding new deployment and maintenance features:
- The Windows Imaging Format (WIM) provides the cornerstone of Microsoft's new deployment and packaging system. WIM files, which contain a HAL-independent image of Windows Vista, can be maintained and patched without having to rebuild new images. Windows Images can be delivered via Systems Management Server or Business Desktop Deployment technologies. Images can be customized and configured with applications then deployed to corporate client personal computers using little to no touch by a system administrator. ImageX is the Microsoft tool used to create and customize images.
- Windows Deployment Services replaces Remote Installation Services for deploying Vista and prior versions of Windows.
- Approximately 700 new Group Policy settings have been added, covering most aspects of the new features in the operating system, as well as significantly expanding the configurability of wireless networks, removable storage devices, and user desktop experience. Vista also introduced an XML-based format (ADMX) to display registry-based policy settings, making it easier to manage networks that span geographic locations and different languages.[92]
- Services for UNIX, renamed as "Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications", comes with the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista. Network File System (NFS) client support is also included.
- Multilingual User Interface–Unlike previous versions of Windows (which required the loading of language packs to provide local-language support), Windows Vista Ultimate and Enterprise editions support the ability to dynamically change languages based on the logged-on user's preference.
- Wireless Projector support
Developer[edit]
Windows Vista includes a large number of new application programming interfaces. Chief among them is the inclusion of version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, which consists of a class library and Common Language Runtime and OS/2 environment just like its NT predecessors. Version 3.0 includes four new major components:[93]
These technologies are also available for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to facilitate their introduction to and usage by developers and end users.
There are also significant new development APIs in the core of the operating system, notably the completely re-designed audio, networking, print, and video interfaces, major changes to the security infrastructure, improvements to the deployment and installation of applications ("ClickOnce" and Windows Installer 4.0), new device driver development model ("Windows Driver Foundation"), Transactional NTFS, mobile computing API advancements (power management, Tablet PC Ink support, SideShow) and major updates to (or complete replacements of) many core subsystems such as Winlogon and CAPI.
There are some issues for software developers using some of the graphics APIs in Vista. Games or programs built solely on the Windows Vista-exclusive version of DirectX, version 10, cannot work on prior versions of Windows, as DirectX 10 is not available for previous Windows versions. Also, games that require the features of D3D9Ex, the updated implementation of DirectX 9 in Windows Vista are also incompatible with previous Windows versions.[95] According to a Microsoft blog, there are three choices for OpenGL implementation on Vista. An application can use the default implementation, which translates OpenGL calls into the Direct3D API and is frozen at OpenGL version 1.4, or an application can use an Installable Client Driver (ICD), which comes in two flavors: legacy and Vista-compatible. A legacy ICD disables the Desktop Window Manager, a Vista-compatible ICD takes advantage of a new API, and is fully compatible with the Desktop Window Manager.[96] At least two primary vendors, ATI and NVIDIA provided full Vista-compatible ICDs.[97] However, hardware overlay is not supported, because it is considered as an obsolete feature in Vista. ATI and NVIDIA strongly recommend using compositing desktop/Framebuffer Objects for same functionality.[98]
Installation[edit]
Windows Vista is the first Microsoft operating system:
Removed features[edit]
Some notable Windows XP features and components have been replaced or removed in Windows Vista, including several shell and Windows Explorer features, multimedia features, networking related functionality, Windows Messenger, NTBackup, the network Windows Messenger service, HyperTerminal, MSN Explorer, Active Desktop, and the replacement of NetMeeting with Windows Meeting Space. Windows Vista also does not include the Windows XP "Luna" visual theme, or most of the classic color schemes that have been part of Windows since the Windows 3.x era. The "Hardware profiles" startup feature has also been removed, along with support for older motherboard technologies like the EISA bus, APM and game port support (though on the 32-bit version game port support can be enabled by applying an older driver).[102] IP over FireWire (TCP/IP over IEEE 1394) has been removed as well.[103] The IPX/SPX protocol has also been removed, although it can be enabled by a third-party plug-in.[104]
Editions[edit]
Windows Vista shipped in six different editions.[105]
Sup91;5993;supppThe Live Music Archive sub-collection includes more than 170,000 concert recordings from independent musicians, as well as more established artists and musical ensembles with permissive rules about recording their concerts, such as the Grateful Dead, and more recently, The Smashing Pumpkins. Also, Jordan Zevon has allowed the Internet Archive to host a definitive collection of his father Warren Zevon's concert recordings. The Zevon collection ranges from 19762001 and contains 126 concerts including 1,137 songs.
sup91;6093;supppThe Great 78 Project aims to digitize 250,000 78 rpm singles (500,000 songs) from the period between 1880 and 1960, donated by various collectors and institutions.
.What’s New in the 123 OutLook Express Backup Enterprise Edition v1.20 by RiSE serial key or number?
Screen Shot
System Requirements for 123 OutLook Express Backup Enterprise Edition v1.20 by RiSE serial key or number
- First, download the 123 OutLook Express Backup Enterprise Edition v1.20 by RiSE serial key or number
-
You can download its setup from given links:


