
Wise Application Integration Suite v2.01 serial key or number

Wise Application Integration Suite v2.01 serial key or number
Arta Software License Key
How to Prepare Test Plan and Write Test Cases for ERP Application – ERP Testing Part-2
In the previous article, we have seen few key points of ERP like the real meaning of the term ERP, various modules of ERP, the importance of ERP testing, the criticalities of ERP testing and a road-map for the preparation of the ERP testing.
=> Check ERP testing part 1 tutorial here.
In this article, let’s get into more practical details on ERP (SAP) Testing like preparing the quality assurance plan, test plan, test suite, test cases and test execution strategy.
=> Click Here For Complete Test Plan Tutorial Series
This tutorial is a good example for writing test plan from scratch for any application. We have also provided sample test suite template for download.
For the demonstration purpose, let us assume the ERP application under testing consists of the following modules with some key information about the implementation plan as below.
ERP Name: ABC Manufacturing ERP
Customer Name: XYZ Petrochemicals LLC
Industry Verticals: Manufacturing
Corporate Office: New York
Branch Offices: Los Angeles and Chicago
Production Plant: Houston
Inventory Warehouses: Houston, Los Angeles, and Chicago
Total Employees: 2500
System Users: 325
Company Turnover: USD 1M
Departments: Administration, Finance, Accounts, HR, Production, Quality, Stores, Sales, Marketing, Maintenance, Dispatch, Customer Support
Modules: Budget, CRM, Customer, Vendor, Sales, Purchase, Payments, Contracts, Finance, Accounts, Human Capital, Payroll, Production Planning, Project Management, Inventory, Material Management, Work Orders, Fixed Asset, Business Intelligence
Delivery Model: On-Premise and Cloud
Implementation Plan: Requirements Gathering, Business Workflow Analysis, Data Flow Assessment, Customization and Enhancement, Delivery and Rollout, End User Training
Find below some of the screenshots of the ERP software application for some important business process like Sales Order, Customer Financials, Payments Header, Fixed Asset, Employee Management and Sales Report which will give an idea about the criticality and complexity of the ERP testing.
(Note: Click on any image for enlarged view)
Screenshot 1: Sales Order
Screenshot 2: Sales Order (US)
Screenshot 3: Customer Financials
Screenshot 4: Payments Header (India)
Screenshot 5: Payments Header (US)
Screenshot 6: Fixed Asset (India)
Screenshot 7: Fixed Asset (US)
Screenshot 8: Employee Management
Screenshot 9: Sales Report
What You Will Learn:
ERP QA Plan
Assuring Quality is a major milestone of any ERP implementation project, which consists of the following stakeholders and success depends on dedicated efforts by all as a “Team”.
The stakeholders of ERP implementation project might be:
- Implementation Team – Consists of the team of professionals from ERP Company or from the local implementation partner. Must have implementation expertise.
- Software Vendor – Software suppliers for the operating system, database and other office applications required for ERP.
- Hosting Provider – Hosting providers for the servers, network, internet and intranet infrastructure required for ERP implementation. Must have implementation expertise.
- Business Team – Consists of the team from the business development or the management steering committee.
- Technical Team – The development team or the implementation team to be available throughout the course of the project. Must have implementation expertise.
- Testing Team – The testing team from the ERP Company or from the local partners having expertise on the ERP implementation strategies.
- Customer Team – The end user team or the departmental heads, who have the complete working knowledge of the business process.
As we discussed in the previous tutorial, testing the ERP (e.g SAP) software application is different than testing the other software applications. ERP applications are domain specific and industry-specific. The common modules like Finance, Accounting, Inventory, Fixed Asset, Sales, Purchase, Human Capital, and Payroll are available in all the ERP systems.
Apart from these common modules, few industrial specific modules are available as per the targeted customers. For example, a “manufacturing ERP” may have a “production planning” module, a “pharma ERP” may have a “doctor-patient” module and an “education ERP” may have a “student” module and so on.
So, the quality factor should be enabled with some pre-defined metrics to be shared well in advance with all the stakeholders in the above list.
To maintain the quality, stakeholders are mutually got into service level agreements. All the stakeholders as a team should have the defined action items, responsibilities with the target dates to achieve the expected quality of statement of work.
ERP Test Plan
ERP test plan should consist of the following information for an effective and successful implementation.
The test plan has the objectives, quality metrics, features to be tested manually, features to be tested through automation tools, project environment, team infrastructure, resource requirements, testing schedule, testing deliverables, test execution infrastructure, testing framework, assumptions, dependencies, constraints, bug tracking mechanism, bug reporting tools and acceptance criteria etc.,
Below is the sample test plan for our ERP implementation project for XYZ Petrochemical LLC.
See also – if you need more information on how to write test plan please check these tutorials:
Project Description
ABC Manufacturing ERP is an integrated ERP solution for the manufacturing industry. The product consists of the core modules like Accounting, Finance, Budget, Inventory, Fixed Asset, Customers, Vendors, CRM, Sales, Purchase, Payments, Contracts, Human Capital, Payroll, Production Planning, Project Management, Inventory, Material Management, Work Orders and Business Intelligence.
The customer’s vertical is into manufacturing and their business is manufacturing petrochemical bi-products and selling them to the domestic and international clients. The raw materials are purchased from domestic and international markets. The company operates from New York, the USA with branches in various parts of the Country.
The company also have warehouses at remote locations. The ERP system will be implemented in a centralized location at the corporate premises and connect the other branches, warehouses, production plants, marketing offices from various parts of the Country through Internet, WAN, Wi-Fi, Cloud Infrastructure. The proposed solution supports multiple languages like English (for International customers, Hindi (for IN users), Arabic (for Middle East vendors) and supports multiple currency transactions.
The system also has an E-Commerce customer portal for online sales orders with credit card payment gateway and a Vendor portal for purchase quotations. There are more than 300 system users going to use the system from various parts of the globe with at least more than 10,000 transactions per day.
Objective
- Identify the modules to be tested manually.
- Identify the modules to be tested through automation tools.
- Define the testing strategy, testing scope and testing activities.
- Define testing criteria, assumptions, dependencies and constraints.
- Identify the testing team, their allocation, and their testing schedule.
- Setup the manual and automation testing framework.
- Setup the testing infrastructure with the software and hardware configuration.
- Define the stakeholders of the project for ERP implementation.
- Define the communication and escalation mechanism.
- Define the work environment, task details, and the responsibilities.
- Risk management with risk mitigation plans.
- Define the test deliverables and the reporting tools.
Module wise Features for Manual Testing
- Payments Module (Payment Creation, Approve Payments, Issue Cheques)
- Funding Module (Joint Payments, Approve Joint Payments, Issue Cheques)
- Payroll Module (Payroll Cheques, Issue Cheques)
- Fixed Assets Module (Asset Depreciation, Asset Disposal)
- …
Module wise Features for Automation Testing
- Sales Module (Sales Order, Shipping Sales Order, Backorders, Sales Invoicing)
- Purchase Module (Purchase Contract, Purchase Orders, Purchase Amendments)
- Customer Module (Customer Management, Customer Financials)
- Human Capital Module (Employee Management, Attendance, Loans, Leaves)
- …
Features to be Tested Off Premises
- Functionality Testing: All the functional test cases of all modules, which are reviewed and approved.
- Regression Testing: All the functional test cases for the customized modules, which are reviewed and approved.
- Smoke Testing: All the functional test cases marked for Sanity, which is reviewed, executed and approved.
- …
Features to be Tested On Premises
- System Testing: All the system test cases of all modules, which are reviewed and approved.
- Integration Testing: All the system test cases of all modules, which are reviewed and approved.
- Performance Testing: All the performance test cases, which are reviewed and approved.
- Load Testing: All the load test cases, which are reviewed and approved.
- User Acceptance Testing: All the user acceptance testing, which are reviewed and approved.
- …
Features to be Tested on Mobile, Wi-Fi & Cloud
Functionality Testing: All the system test cases of the CRM module, which are reviewed and approved.
Resource Requirements
Testing Schedule
Test Case Execution
Test Coverage
A: Functional Testing, B: System Testing, C: Integrity Testing, D: Security Testing, E: Usability Testing, F: Performance Testing, G: Interface Testing, H: Installation Testing
Deliverables
Risk Management
Issue Tracker
Confluence and JIRA tools are used for issue tracking in the project. Also, JIRA is customized and configured for all the testing team members to escalate issue and report bugs and assigned to the concern development team with the responsibility and target dates.
Quality Metrics
ERP Test Suite
Like the normal testing process, ERP Test Suite is normally prepared as an Excel document. This document controls the complete revision history of the various test suites of all the modules in ERP application. The test cases of each module, test execution history, list of bugs and the test report history are maintained in an ERP test suite.
For automation testing, the “test scripts” are maintained in the test suite and the related iteration of test execution history is maintained. Depends on the type of testing and the complexity of the test cases, automation test scripts are maintained in the suite which should be designed in such a way for re-usability.
Find below the snapshot of an ERP test suite in excel document.
Sample Test Suite Template Download:
Below is sample test suite template for download. It contains templates for revision history, test report, bug report, smoke test cases, regression test cases
=> Click here to Download ERP test suite template.
ERP Test Cases
Apart from the functional test cases, regression test cases, sanity/smoke test cases, ERP Testing requires other type of test cases for installation testing, configuration testing, implementation testing, adaptability testing, network testing, server testing, offline testing, remote testing, multi-currency testing, multi-language testing, device testing, intranet testing, real-time testing etc.,
Most important, ERP being a centralized automated solution, being accessed by multiple users concurrently online in real time, which involves a financial transaction, each and every test cases should be written with a lot of dedicated effort and real-time data.
Also, the test execution status should be updated as “Pass” after verifying the output data with the predefined real-time data. So, the test cases should always have a column for “test data” and “output data”.
Sample Test Scenario:
Find below a sample test case for our ERP demonstration This test cases may consist of a lot of small test cases which can segregate and maintained, but for demo purpose, it’s combined with a single test case.
Conclusion
ERP Testing is having a lot of risks and complexities compared to any software/product testing. Also, managing the quality metrics in ERP implementation projects requires a lot of attention and dedicated efforts as a “team” from the multiple stakeholders.
Testing professionals need to understand the difference between the quality of the product and the quality of implementation. ERP testing requires trusted sponsorship on time and budget from the management and the customers. Testing should be done by the ERP expert team and should not be allocated to an inexperienced team for any reason.
It is very important to use the universally proven right process, methodologies, approaches, and automated tools. We should not assume that “automation” completely replaces the “manual” testing, but should not compromise on using the required testing infrastructure and framework. Don’t underestimate the time required for collecting live real data from the customers.
For Testing Professionals, this journey is “Excellent Resource for ERP Product Testing!”.
Let us know if you have any questions on ERP or in particular SAP Testing.
=> Visit Here For Complete Test Plan Tutorial Series
PREV Tutorial | NEXT Tutorial
Cisco Smart Licensing - Troubleshooting Steps and Considerations on Catalyst platforms
1. Introduction
1.1. What is Cisco Smart Licensing?
Cisco Smart Licensing is a cloud-based unified license management system that manages all of the software licenses across Cisco products. It enables customers to purchase, deploy, manage, track and renew Cisco Software licenses. It also provides information about license ownership and consumption through a single user interface
The solution is comprised of online Smart Accounts (at Cisco Smart Licensing Portal) used for tracking Cisco software assets and the Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) which is used to manage the Smart Accounts. CSSM is where all licensing management related tasks, such as registering, de-registering, moving, and transferring licenses can be performed. Users can be added and given access and permissions to the smart account and specific virtual accounts.
To learn more about Cisco Smart Licensing, visit:
a) Cisco Smart Licensing home page
b) Cisco Community - On-Demand Trainings.
Smart accounts can be created here: Smart Accounts
Smart accounts can be managed here: Smart Software Licensing
1.2. Smart Licensing Implementation Methods
There are multiple methods in deploying Cisco Smart Licensing that can be leveraged depending on a company’s security profile such as:
Direct Cloud Access
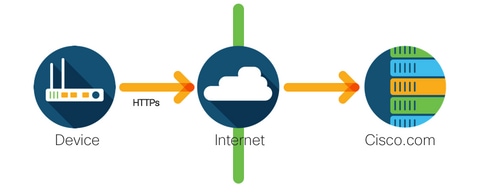
Cisco products send usage information directly over the Internet securely using HTTPS. No additional components are needed.
Access through an HTTPS Proxy

Cisco products send usage information through an HTTP proxy server securely using HTTPS. An existing proxy server can be used or this can be deployed through Cisco's Transport Gateway. (click here for some additional information).
On-premise License Server (Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite)
Cisco products send usage information to an on-premise server instead of directly over the internet. Once a month the server reaches out over the internet for all devices via HTTPS or can be manually transferred to synchronize its database. CSSM Satellite is available as a Virtual Machine (VM) and can be downloaded here. For additional information, visit Smart Software Manager Satellite page.
1.3. Supported IOS XE Platforms
- From 16.9.1 release onwards, the Catalyst 3650/3850 and Catalyst 9000 series switch platforms support the Cisco Smart Licensing method as the only licensing method.
- From 16.10.1 release onwards, router platforms such as the ASR1K, ISR1K, ISR4K, and virtual routers (CSRv / ISRv) support the Cisco Smart Licensing method as the only licensing method.
1.4. Migration from Legacy Licenses to Smart Licenses
There are two methods for converting a legacy license, like Right-To-Use (RTU) or Product Activation Key (PAK) to a Smart License. For details on which method needs to be followed please refer to the relevant release notes and/or configuration guide for the specific Cisco device.
1.4.1. Converting through Device Led Conversion (DLC)
- Device Led Conversion (DLC) is a one-time method where the Cisco Product can report what licenses it is using and the licenses are automatically deposited into their corresponding Smart Account on the Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM). The DLC procedure is performed directly from the Command Line Interface (CLI) of the specific Cisco device.
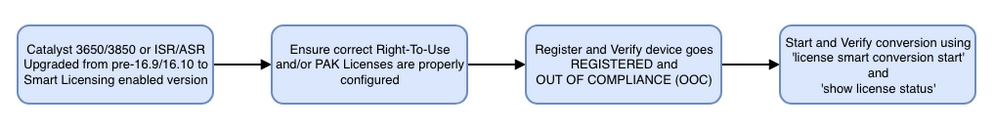
1.4.2. Converting through Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) or License Registration Portal (LRP)
Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) Method:
1. Login to Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) at https://software.cisco.com/
2. Navigate to Smart Software Licensing > Convert to Smart Licensing
3. Select Convert PAK or Convert Licenses
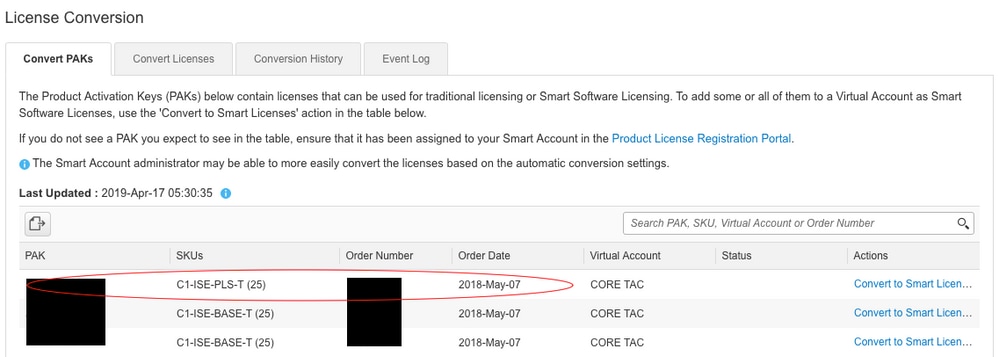
4. Locate the license in the table below if converting PAK license. If converting a non-PAK license use the "License Conversion Wizard" for step by step directions.
Location of known PAK files associated with Account:
Location of "License Conversion Wizard" link:
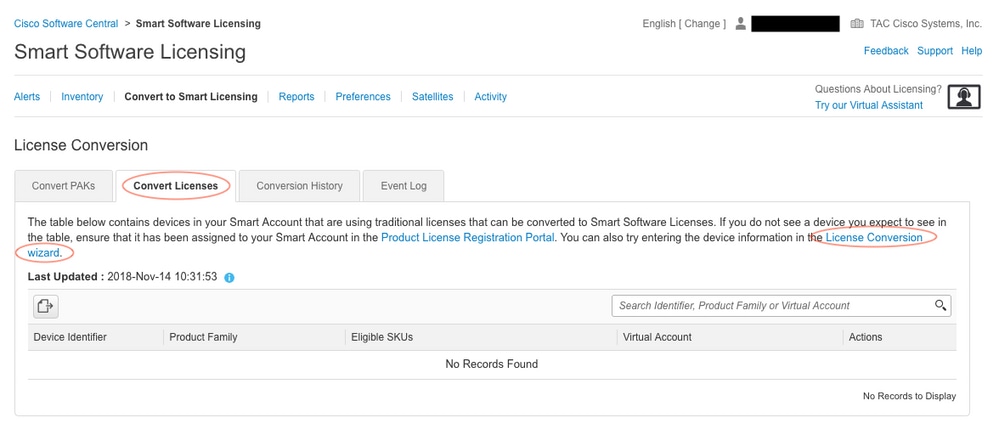
5. Locate the Desired License and Product combination
6. Click (under Actions): Convert to Smart Licensing
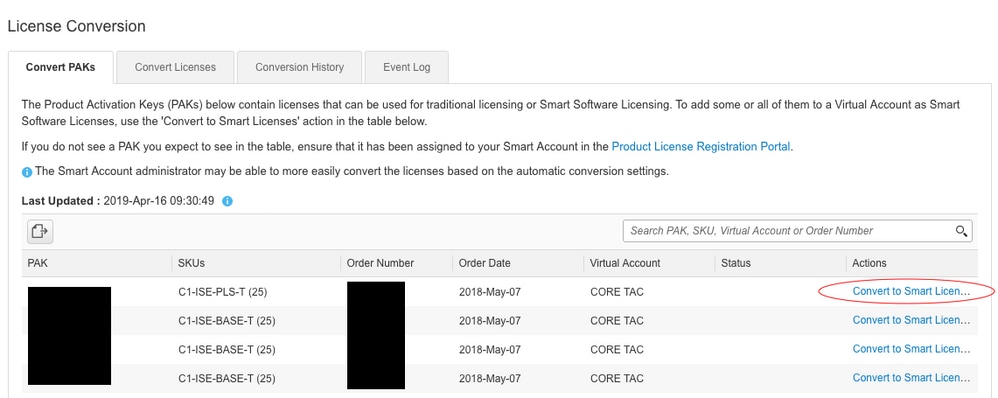
7. Select desired virtual account, license, and click Next
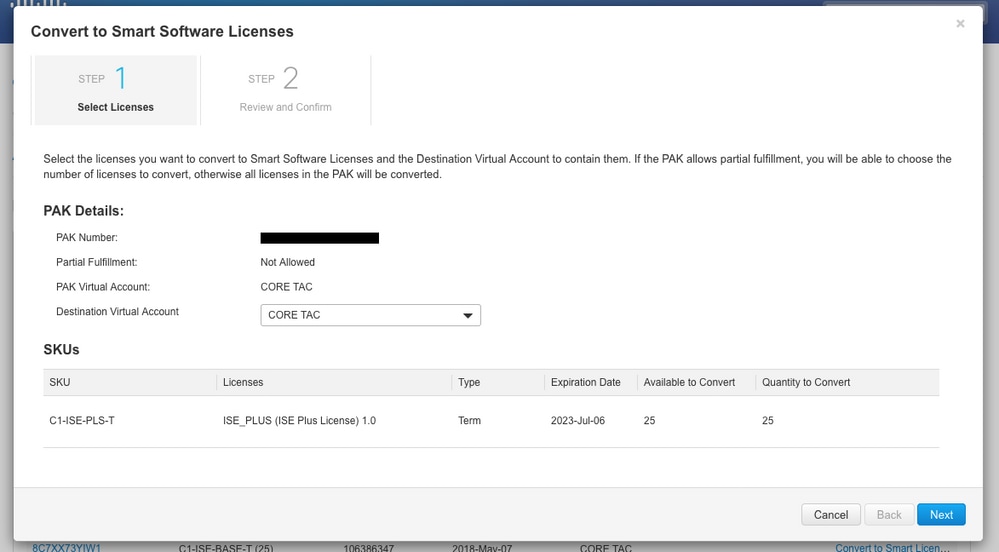
8. Review Selections, then click Convert Licenses
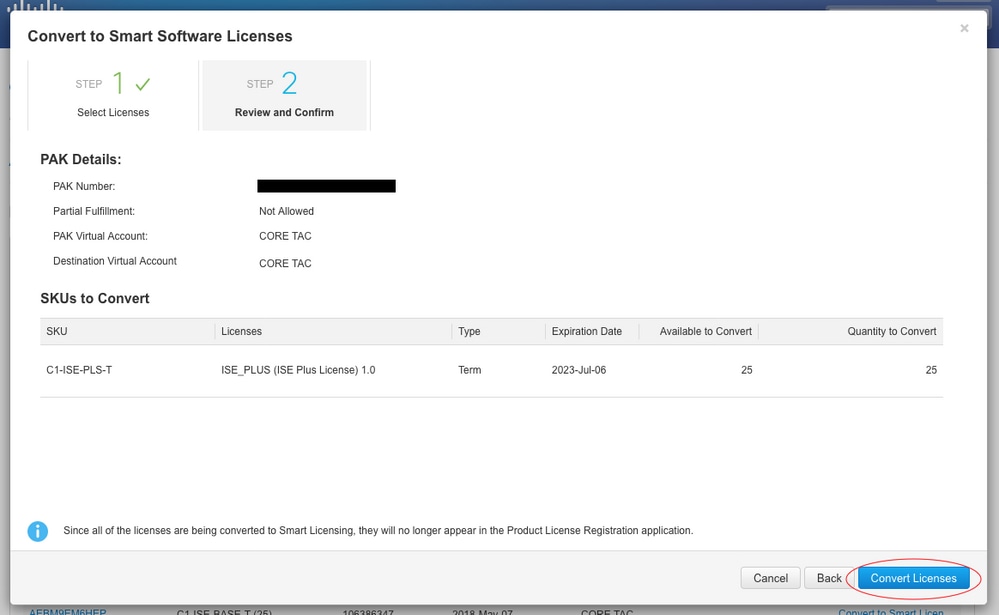
1.4.3. Converting through contacting Cisco Global Licensing Operations (GLO) department
The Global Licensing Operations department can be reached here at our worldwide contact centers.
2. Configuration
2.1. Basic configuration
Exact procedure how to configure Smart Licensing can be found in System Management Configuration Guide available for each release / platform.
For example: System Management Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Fuji 16.9.x (Catalyst 9300 Switches)
2.2. Registration Token / Device ID Token
Before registering device, Token needs to be generated. The registration token, also known as the device id token, is a unique token generated from the smart licensing portal or Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite when initially registering a Cisco device to the corresponding smart account. An individual token can be used to register multiple Cisco devices depending on the parameters used during creation.
The registration token is also only required during initial registration of a Cisco device as it provides the information to the device to call-home to the Cisco back end and be tied to the correct Smart Account. After the Cisco device is registered the token is no longer required.
For more information in regard to registration tokens and how they are generated, please click here for a general guide. For more details, please refer to the configuration guide for the specific Cisco device.
2.3. Registration and License States
While deploying and configuring Smart Licensing there are multiple possible states that a Cisco device can be in. These states can be displayed by looking at show license all or show license status from the Command Line Interface (CLI) of the Cisco device.
Below is a list of all states and their meaning:
- Evaluation (Unidentified) State
- This is a default state of the device when first booted.
- Usually, this state is seen when a Cisco device has not yet been configured for Smart Licensing or registered to a Smart Account.
- In this state all features are available and the device can freely change license levels.
- The evaluation period is used when the device is in the unidentified state. The device will not attempt to communicate with Cisco in this state.
- This will be 90 days of usage and not 90 calendar days. Once it is expired it is never reset.
- There is one evaluation period for the entire device it is not per entitlement
- When the evaluation period expires at the end of 90 days, the device goes in to EVAL EXPIRY mode, however there is no functional impact or disruption in functionality, even after reload. Currently there is no enforcement in place.
- The countdown time is maintained across reboots.
- The evaluation period is used if the device has not yet registered with Cisco and has not received the following two messages from the Cisco backend:
- Successful response to a registration request
- Successful response to an entitlement authorization request.
- Registered State
- This is the expected state after successfully completing registration.
- The Cisco device has been able to successfully communicate with a Cisco Smart Account and register.
- The device receives an ID certificate valid for 1 year which will be used for future communications
- The device will send a request to CSSM to authorize the entitlements for the licenses in use on the device
- Depending on the CSSM response the device will then enter Authorized or Out of Compliance
- The Id certificate expires at the end of one year. After 6 months the software Agent process will try to renew the certificate. If the Agent cannot communicate with the Cisco Smart Software Manager it will continue to try and renew the Id certificate until the expiration date (1 year). At the end of one year, the agent will go back to the Un-Identified state and will try to enable the Evaluation period. The CSSM will remove the product instance from its database.
- Authorized State
- This is the expected state when device is using an entitlement and is in Compliance (no negative balance),
- The Virtual Account on CSSM had the correct type and number of licenses to authorize the consumption of the device’s licenses
- At the end of 30 days, the device will send a new request to CSSM to renew the authorization.
- Has a time span of 90 days after which (if not successfully renewed) is moved to Authorization Expired state.
- Out of Compliance State
- This is the state when device is using an entitlement and is not in Compliance (negative balance),
- This state is seen when the license does not have an available license in the corresponding Virtual Account that the Cisco device is registered to in the Cisco Smart Account.
- To enter into Compliance / Authorized state, a customer must add the correct number and type of licenses to the Smart Account
- When in this state the device will automatically send an authorization renewal request every day
- Licenses and features will continue to operate and there is no functional impact
- Authorization Expired State
- This is the state when device is using an entitlement has not been able to communicate with the Cisco Smart Account associated for over 90 days.
- This is typically seen if the Cisco device loses internet access or cannot connect to tools.cisco.com after initial registration.
- Online methods of smart licensing require Cisco devices to communicate a minimum of every 90 days to prevent this status.
- CSSM will return all in use licenses for this device back to the pool since it has not had any communications for 90 days
- While in this state the device will continue to try to contact Cisco, every hour, to renew the entitlement authorization, until the registration period (id certificate) expires
- If the software Agent re-establishes communications with Cisco and receives to its request for authorization it will process that reply normally and enter into one of the established states
3. Considerations and Caveats
- Starting in 16.9.1 for switches and 16.10.1 for routers, a default Call-home profile named "CiscoTAC-1" is generated to assist with migrating to Smart Licensing. By default, this profile is set up for the Direct Cloud Access method.
- When utilizing a Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite, the destination address under the active call-home configuration must point to it (case-sensitive!):
(cfg-call-home)#profile "CiscoTAC-1"
(cfg-call-home-profile)#destination address http https://<IP/FQDN>/Transportgateway/services/DeviceRequestHandler
- If DNS needs to be resolved in a VRF, then DNS can be configured in the following way:
(config)#ip name-server [vrf <VRF>] <IP>
Alternatively, if DNS is not available, statically configure local DNS to IP mapping (based on local DNS resolution on your end-device) or replace DNS name in call-home configuration with IP address. Refer to example for direct cloud access (for Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite use its own DNS name instead of tools.cisco.com):
(config)#ip host tools.cisco.com 173.37.145.8- If communication to tools.cisco.com needs to be originated from the interface in specific VRF (e.g. Mgmt-vrf), then the following CLI needs to be configured:
- A different number of licenses might be consumed depending on the configuration of the Cisco device such as with Catalyst switches running in StackWise or StackWise Virtual:
Traditional Stack-wise Supported Switches (e.g. Catalyst 9300 series):
Network License: 1 license is consumed per switch in the stack
DNA License: 1 license is consumed per switch in the stack
Modular Chassis (e.g. Catalyst 9400 series):
Network License: 1 license is consumed per supervisor in the chassis
DNA License: 1 license is consumed per chassis
Fixed Stack-wise Virtual Supported Switches (e.g. Catalyst 9500 series):
Network License: 1 license is consumed per switch in the stack
DNA License: 1 license is consumed per switch in the stack
- Only one call-home profile can be active for Smart Licensing.
- Licenses are only consumed if a corresponding feature is configured.
- Cisco devices configured for Smart Licensing need to be configured with the correct system time and date to ensure they are properly synchronized with the corresponding Cisco Smart Account. If the time offset of the Cisco device is too far off it, the device can fail to register. The clock will need to be manually set or configured via a timing protocol such as Network Time Protocol (NTP) or Precision Time Protocol (PTP). For the exact steps required to implement these changes please refer to the configuration guide for the specific Cisco device.
- The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) key generated during the Cisco device registration needs to be saved if it is not automatically saved after registration. If the device fails to save the PKI key then a syslog is generated stating to save the configuration via “copy running-config startup-config” or “write memory”.
- If the PKI key of the Cisco device is not properly saved, then the license state can be lost on failovers or reloads.
- Smart Licensing does not support HTTPS Proxy SSL certificate interception by default when using 3rd party proxies for the HTTPS Proxy method. To support this feature, you can either disable SSL interception on the Proxy, or manually import the certification sent from the Proxy.
Note, the certificate will need be in a BASE64 format to be copied and pasted onto the device as a TrustPoint.
The following example shown below uses "LicRoot" as the TrustPoint name, however, this name can be changed as desired.
Device#conf t
Device(config)#crypto pki trustpoint LicRoot
Device(ca-trustpoint)#enrollment terminal
Device(ca-trustpoint)#revocation-check none
Device(ca-trustpoint)#exit
Device(config)#crypto pki authenticate LicRoot
Enter the base 64 encoded CA certificate.
End with a blank line or the word "quit" on a line by itself
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
Certificate has the following attributes:
Fingerprint MD5: XXXXXXXX
Fingerprint SHA1: XXXXXXX
% Do you accept this certificate? [yes/no]: yes
Trustpoint CA certificate accepted.
% Certificate successfully imported
- When using the Transport Gateway HTTP Proxy the IP address needs to be changed from tools.cisco.com to the Proxy like the following:
destination address http https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEService
TO
destination address http https://<TransportGW-IP_Address>:<port_number>/Transportgateway/services/DeviceRequestHandler - The Transport Gateway IP address can found by navigating to the HTTP Settings and looking under the HTTP Service URLs on the Cisco Transport Gateway GUI.
- For more information please see the following configuration guide for the Cisco Transport Gateway here.
4. Troubleshooting
When migrating a Cisco device to a Smart Licensing enabled software version the following flowchart can be used as a general guide for all three methods (Direct Cloud Access, HTTPS Proxy, and Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite).
Device Upgraded or Shipped with software release that supports Smart Licensing (refer to section 1.3 for list of supported IOS-XE releases).
Below troubleshooting steps mainly concentrate on a scenario in which 'device fails to register'.
4.1. Device Fails to register
After initial configuration, in order to enable Smart Licensing, Token, which is generated on CSSM / Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite, needs to be registered on the device via CLI:
license smart register idtoken <TOKEN>This should generate the following events:
!! Smart licensing process starts
!
Registration process is in progress. Use the 'show license status' command to check the progress and result !
! Crypto key is automatically generated for HTTPS communication
!
Generating 2048 bit RSA keys, keys will be exportable... [OK] (elapsed time was 1 seconds) %CRYPTO_ENGINE-5-KEY_ADDITION: A key named SLA-KeyPair has been generated or imported by crypto-engine %PKI-4-NOCONFIGAUTOSAVE: Configuration was modified. Issue "write memory" to save new IOS PKI configuration !
! Call-home start registration process
! %CALL_HOME-6-SCH_REGISTRATION_IN_PROGRESS: SCH device registration is in progress. Call-home will poll SCH server for registration result. You can also check SCH registration status with "call-home request registration-info" under EXEC mode. !
! Smart Licensing process connects with CSSM and check entitlement.
! %SMART_LIC-6-EXPORT_CONTROLLED: Usage of export controlled features is allowed %SMART_LIC-6-AGENT_REG_SUCCESS: Smart Agent for Licensing Registration with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellitefor udi PID:<PID>,SN:<SN> %SMART_LIC-4-CONFIG_NOT_SAVED: Smart Licensing configuration has not been saved %SMART_LIC-5-IN_COMPLIANCE: All entitlements and licenses in use on this device are authorized %SMART_LIC-6-AUTH_RENEW_SUCCESS: Authorization renewal with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite. State=authorized for udi PID:<PID>,SN:<SN>
To check call-home configuration, run the following CLI:
#show call-home profile all Profile Name: CiscoTAC-1 Profile status: ACTIVE Profile mode: Full Reporting Reporting Data: Smart Call Home, Smart Licensing Preferred Message Format: xml Message Size Limit: 3145728 Bytes Transport Method: http HTTP address(es): https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEService Other address(es): default Periodic configuration info message is scheduled every 1 day of the month at 09:15 Periodic inventory info message is scheduled every 1 day of the month at 09:00 Alert-group Severity ------------------------ ------------ crash debug diagnostic minor environment warning inventory normal Syslog-Pattern Severity ------------------------ ------------ APF-.-WLC_.* warning .* majorTo check Smart Licensing status, run the following CLI:
#show license summary Smart Licensing is ENABLED Registration: Status: REGISTERED Smart Account: TAC Cisco Systems, Inc. Virtual Account: Krakow LAN-SW Export-Controlled Functionality: ALLOWED Last Renewal Attempt: None Next Renewal Attempt: Nov 22 21:24:32 2019 UTC License Authorization: Status: AUTHORIZEDLast Communication Attempt: SUCCEEDED Next Communication Attempt: Jun 25 21:24:37 2019 UTC License Usage: License Entitlement tag Count Status ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- C9500 Network Advantage (C9500 Network Advantage) 1 AUTHORIZED C9500-DNA-40X-A (C9500-40X DNA Advantage) 1 AUTHORIZEDIn case device fail to register (and Status is different from REGISTERED as shown above; note that Out-of-Compliance points to an issue on CSSM like missing license in Smart Virtual Account, incorrect mapping (i.e. Token from different virtual account was used where licenses are not available, etc.) check the following:
1. Verify configuration settings and common failure scenarios
Refer to section 2.1 for basic configuration steps. Look also at section 5 for common failure scenarios observed in the field.
2. Check basic connectivity
Verify that device can reach (and open TCP port) to tools.cisco.com (in case of direct access) or to Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite:
#show run all | in destination address http destination address http https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEService ! ! check connectivity ! #telnet tools.cisco.com 443 /source-interface gi0/0 Trying tools.cisco.com (173.37.145.8, 443)... Open [Connection to tools.cisco.com closed by foreign host]In case above does not work, double-check your routing rules, source-interface and firewall settings.
Note that HTTP (TCP/80) is being deprecated and the recommended protocol is HTTPS (TCP/443).
Refer to section: "3. Considerations and Caveats" in this document for further guidelines how to configure DNS and HTTP details.
3. Verify Smart License settings
Collect the output of:
#show tech-support licenseand validate collected configuration / logs (attach this output in case you decide to open Cisco TAC case for further investigation).
4. Enable debugs
Enable the following debugs to collect additional information about Smart Licensing process (note that after enabing debugs, you need to try to register license once again via CLi mentioned in point 4.1):
#debug call-home smart-licensing [all | trace | error] #debug ip http client [all | api | cache | error | main | msg | socket]For internal debugs, enable and read binary traces:
! enable debug #set platform software trace ios [switch] active R0 infra-sl debug ! ! read binary traces infra-sl process logs #show platform software trace message ios [switch] active R05. Common Failure Scenarios
The following are some common failure scenarios that could be experienced during or after a Cisco device registration:
Scenario #1: Switch Registration "Failure Reason: Product Already Registered"
Snip of "show license all":
Registration:
Status: UNREGISTERED - REGISTRATION FAILED
Export-Controlled Functionality: NotAllowed
Initial Registration: FAILED on Oct 22 14:25:31 2018 EST
Failure reason: Product Already Registered
Next Registration Attempt: Oct 22 14:45:34 2018 EST
Next Steps:
- The Cisco device will need to be registered again.
- If the Cisco device is seen in the Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM), the "force" parameter will need to be used (i.e. "license smart register idtoken <TOKEN> force")
NOTE: The failure reason can also show as the following:
- Failure reason: The product <X> and sudi containing udiSerialNumber:<SerialNumber>,udiPid:<Product> has already been registered.
- Failure reason: Existing Product Instance has Consumption and Force Flag is False
Scenario #2: Switch Registration "Failure Reason: Your request could not be processed right now. Please try again"
Snip of "show license all":
Registration:
Status: REGISTERING - REGISTRATION IN PROGRESS
Export-Controlled Functionality: NotAllowed
Initial Registration: FAILED on Oct 24 15:55:26 2018 EST
Failure reason: Your request could not be processed right now. Please try again
Next Registration Attempt: Oct 24 16:12:15 2018 EST
Next Steps:
- Enable debugs as mentioned in section 4 to get more insights on the issue,
- Generate new Token in CSSM in your Smart Licensing and take an another attempt.
Scenario #3: Failure Reason "The device date 1526135268653 is offset beyond the allowed tolerance limit
Snip of "show license all":
Registration:
Status: REGISTERING - REGISTRATION IN PROGRESS
Export-Controlled Functionality: NotAllowed
Initial Registration: FAILED on Nov 1117:55:46 2018 EST
Failure reason: {"timestamp":["The device date '1526135268653' is offset beyond the allowed tolerance limit."]}
Next Registration Attempt: Nov 11 18:12:17 2018 EST
Possible Logs Seen:
%PKI-3-CERTIFICATE_INVALID_NOT_YET_VALID: Certificate chain validation has failed. The certificate (SN: XXXXXX) is not yet valid. Validity period starts on 2018-12-12:43Z
Next Steps:
- Verify that the Cisco device clock is showing the correct time (show clock)
- Configure the Network Time Protocol (NTP) if possible to ensure the clock is set correctly
- If NTP is not possible, verify that the manually set clock (clock set) is correct (show clock) and configured as a trusted time source by verifying that "clock calendar-valid" is configured
NOTE- By default, the system clock is not trusted. "clock calendar-valid" is required.
Scenario #4: Switch Registration "Failure Reason: Communication transport not available."
Snip of "show license all":
Registration: Status: UNREGISTERED - REGISTRATION FAILED
Export-Controlled Functionality: Not Allowed
Initial Registration: FAILED on Mar 09 21:42:02 2019 CST
Failure reason: Communication transport not available.
Possible Logs Seen:
%CALL_HOME-3-CALL_HOME_FAILED_TO_ENABLE: Failed to enable call-home from Smart Agent for Licensing: The command failed to enable smart call home due to an existing active user profile. If you are using a user profile other than "CiscoTAC-1" profile to send data to SCH server in Cisco, please enter "reporting smart-licensing-data" under profile mode to configure that profile for smart licensing. For more details about SCH, please check http://www.cisco.com/go/smartcallhome
%SMART_LIC-3-AGENT_REG_FAILED: Smart Agent for Licensing Registration with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite failed: Communication transport not available.
%SMART_LIC-3-COMM_FAILED: Communications failure with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite: Communication transport not available.
Next Steps:
- Verify that call-home is enabled with "service call-home" in the "show running-config" output of the Cisco device
- Ensure that the correct call-home profile is active
- Verify that "reporting smart-licensing-data" is configured under the active call-home profile
Scenario #5: Switch License Authorization "Failure reason: Fail to send out Call Home HTTP message."
Snip of "show license all":
License Authorization:
Status: OUT OF COMPLIANCE on Jul 26 09:24:09 2018 UTC
Last Communication Attempt: FAILED on Aug 02 14:26:23 2018 UTC
Failure reason: Fail to send out Call Home HTTP message.
Next Communication Attempt: Aug 02 14:26:53 2018 UTC
Communication Deadline: Oct 25 09:21:38 2018 UTC
Possible logs are seen:
%SMART_LIC-3-COMM_FAILED:Communications failure with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite: Fail to send out Call Home HTTP message.
%SMART_LIC-3-AUTH_RENEW_FAILED:Authorization renewal with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite: Communication message send error for udi PID:XXX, SN: XXX
Next Steps:
- Verify that the Cisco device can ping tools.cisco.com or the nslookup translated IP
- Attempt to telnet from the Cisco device to tools.cisco.com on TCP port 443 (port used by HTTPS)
- Verify that the HTTPs client source interface is correct
- Verify that the URL/IP in the call home profile is set correctly on the Cisco device via "show call-home profile all"
- Verify the ip route is pointing to the correct next hop
- Ensure TCP port 443 is not being blocked on the Cisco device, the path to Smart Call Home Server, or the Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite
- Ensure that the correct Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instance is configured if applicable
Scenario #6: Switch License Authorization "Failure reason: Waiting for reply"
Snip of "show license all":
License Authorization:
Status: OUT OF COMPLIANCE on Jul 26 09:24:09 2018 UTC
Last Communication Attempt: PENDING on Aug 02 14:34:51 2018 UTC
Failure reason: Waiting for reply
Next Communication Attempt: Aug 02 14:53:58 2018 UTC
Communication Deadline: Oct 25 09:21:39 2018 UTC
Possible logs are seen:
%PKI-3-CRL_FETCH_FAIL: CRL fetch for trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint failed Reason : Failed to select socket. Timeout : 5 (Connection timed out)
%PKI-3-CRL_FETCH_FAIL: CRL fetch for trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint failed Reason : Failed to select socket. Timeout : 5 (Connection timed out)
Next Steps:
- To correct this issue the SLA-TrustPoint should be configured as none under the running configuration
show running-config
<omitted>
crypto pki trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint
revocation-check none
What is a CRL?
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is a list of revoked certificates. The CRL is created and digitally signed by the certificate authority (CA) that originally issued the certificates. The CRL contains dates for when each certificate was issued and when it expires. Further information in regards to CRL is available here.
Scenario #7: License in "OUT OF COMPLIANCE" status
Snip of "show license all":
License Authorization:
Status: OUT OF COMPLIANCE on Jul 26 09:24:09 2018 UTC
Last Communication Attempt: PENDING on Aug 02 14:34:51 2018 UTC
Failure reason: Waiting for reply
Next Communication Attempt: Aug 02 14:53:58 2018 UTC
Communication Deadline: Oct 25 09:21:39 2018 UTC
Possible logs are seen:
%SMART_LIC-3-OUT_OF_COMPLIANCE: One or more entitlements are out of compliance
Next Steps:
- Verify if Token from proper Smart Virtual Account has been used,
- Verify amount of available licenses here.
Scenario #8: Switch License Authorization "Failure reason: Data and signature do not match "
Snip of "show license all":
License Authorization:
Status: AUTHORIZED on Mar 12 09:17:45 2020 EDT
Last Communication Attempt: FAILED on Mar 12 09:17:45 2020 EDT
Failure reason: Data and signature do not match
Next Communication Attempt: Mar 12 09:18:15 2020 EDT
Communication Deadline: May 09 21:22:43 2020 EDT
Possible logs are seen:
%SMART_LIC-3-AUTH_RENEW_FAILED: Authorization renewal with the Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) : Error received from Smart Software Manager: Data and signature do not match for udi PID:C9000,SN:XXXXXXXXXXX
Next Steps:
- Deregister the switch with "License smart deregister"
- Then register the switch using a new token with "license smart register idtoken <TOKEN> force"
6. References
1) Cisco Smart Licensing home page
2) Cisco Community - On-Demand Trainings.
3) Smart Account - management portal: Smart Software Licensing
4) Smart Account - create new accounts: Smart Accounts
5) Configuration guide (example) - System Management Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Fuji 16.9.x (Catalyst 9300 Switches)
What’s New in the Wise Application Integration Suite v2.01 serial key or number?
Screen Shot
System Requirements for Wise Application Integration Suite v2.01 serial key or number
- First, download the Wise Application Integration Suite v2.01 serial key or number
-
You can download its setup from given links:


